Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma
Updated: 07/03/2023
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
General features
- Usually nodal
- Likely B cell origin
- Two large groups: classical or nodular lymphocyte predominant
- Classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Most common Hodgkin lymphoma
Most likely B cell origin
More common in HIV + population or history of
infectious mononucleosis
Sub classification of classical Hodgkin lymphoma
based on background morphology
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
Uncommon
Probably follicular B cell origin
More common in men
Clinical presentations
- Lymphadenopathy
- B-type symptoms (fever, drenching night sweats, weight loss)
- Other organ involvement: Spleen, liver, lung, bone marrow, etc
- Classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Bimodal age distribution in developed country:
15-35, > 54
Usually lymph nodes: Most common cervical, can
be seen in mediastinal, axillary and paraaotic lymph nodes
Rarely extranodal
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
Indolent
Two age peaks: Children, 30-40
Usually young men with cervical or axillary
adenopathy
Key risk factors
- Classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Immunosuppression
Autoimmune disorders
Family history of Hodgkin lymphoma
Key pathogenesis
- Classical Hodgkin lymphoma
EB virus
Abnormal activation of NF-kB
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
Unclear
Key morphological features
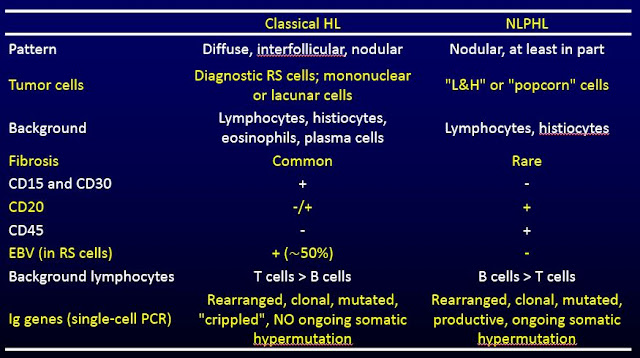
- Classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Reed-Sternberg cells: Binucleate or bilobed
nucleus with large owl-eyed eosinophilic nucleoli; abundant cytoplasm
4 subtypes based on background morphology
- Nodular sclerosis: Sclerosis + mixed inflammatory cells
- Mixed cellularity: Mixed background inflammatory cells, NO sclerosis
- Lymphocyte rich: Predominantly lymphocytes in background
- Lymphocyte depleted: Scattered inflammatory cells, often HIV associated
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
Scattered LP cells (Popcorn cells): Large
lobulated nuclei with nucleoli
Markers
- Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (RS cells)
Positive: CD15, CD30
Negative: CD45
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma(LP cells)
Positive: CD45, CD20
Negative: CD15, CD30
Genetic abnormalities
- Classical Hodgkin lymphoma
IgH gene rearrangement without ongoing
hypermutation
- Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
IgH gene rearrangement with ongoing
hypermutation
Summary
Treatment
- Classical Hodgkin lymphoma: chemotherapy, radiation therapy
- Nodular lymphocytic predominant Hodgkin lymphoma: surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy
Back to lymphoid neoplasms
Back to contents
Comments
Post a Comment