Sepsis
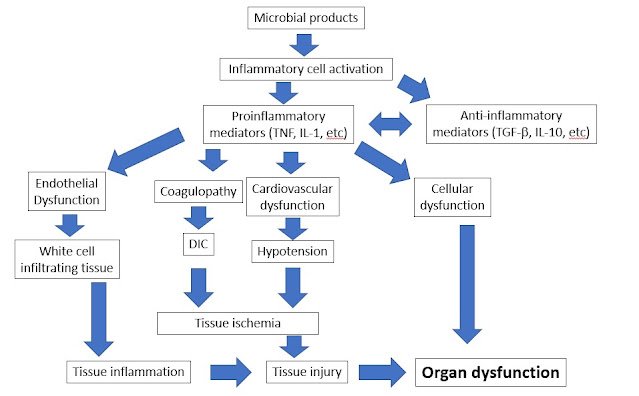
Sepsis Updated: 06/28/2022 © Jun Wang, MD, PhD Definition Life threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection General features Organ dysfunction identified by acute change of 2 or more points in total SOFA score or qSOFA Likely prolonged ICU stay Relatively high mortality rate Commonly associated with infections of injury or internal organs and perforation/rupture of abdominal/pelvic structures Most commonly caused by bacterial infections, but can be caused by virus or fungi Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) A term being abandoned since 2016 Still being used clinically Poor mortality prediction comparing with Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) Clinical responses to either infectious or non-infectious causes Sequential Organ failure Assessment (SOFA) A systemic evaluation of organ function Performed in critically ill patients with suspected sepsis Systems involved o Cardiovascular: Bloo...