Pneumocystis pneumonia
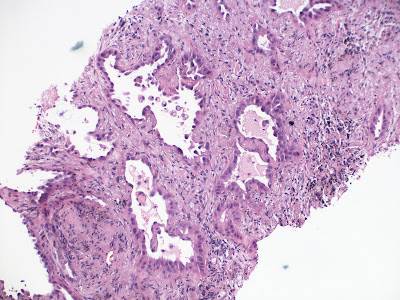
Pneumocystis pneumonia Updated: 08/12/2025 © Jun Wang, MD, PhD General features Caused by the fungus Pneumocystis jirovecii May occur in any immunocompromised patients, such as those with primary immunodeficiency One of the most common AIDS defining diseases Likely airborne transmission High mortality and morbidity Pathogenesis Inhaled pneumocystis attach to alveolar wall Macrophages could not eradicate pneumocystis due to lack of CD4+ lymphocytes Local inflammation results in alveolar injury Clinical presentations Chills, fever, nonproductive cough, difficulty breathing, chest pain, fatigue Radiological findings Usually bilateral diffuse infiltrates Pathological features Foamy eosinophilic material in alveolar spaces Silver stain highlights organisms Diagnosis Identification of pneumocystis jirovecii in bronchoalveolar lavage, sputum, or lung biopsy PCR Managements Trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole Back to pathology of HIV inf...