Practice questions B, intestinal tumors
Practice
questions B, intestinal tumors
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
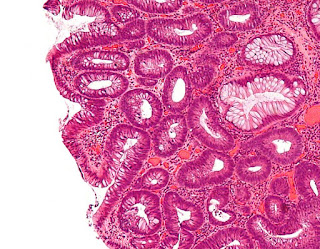
1. Use this case and image for the next four questions. A 15-year-old
boy presents with fatigue vague abdominal pain for a year. He does not have
diarrhea or constipation. He has multiple family members in the paternal side
with early onset colon cancers. Physical exam is unremarkable except pale skin.
No lymphadenopathy is noted. Laboratory tests reveal a hemoglobin of 8.8 g/dl
(normal 12.7-17.7 g/dl) and a positive fecal occult blood test. Image studies
are unremarkable. Colonoscopy exam reveals numerous small pedunculated growths
involving entire colon. Image of biopsy of one of these growths are shown. What
is most likely the diagnosis for the biopsy?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Hyperplastic polyp
B. Intramucosal adenocarcinoma
C. Sessile serrated adenoma
D. Tubular adenoma
E. Villous adenoma
2. A 15-year-old boy
presents with fatigue vague abdominal pain for a year. He does not have
diarrhea or constipation. He has multiple family members in the paternal side
with early onset colon cancers. Physical exam is unremarkable except pale skin.
No lymphadenopathy is noted. Laboratory tests reveal a hemoglobin of 8.8 g/dl
(normal 12.7-17.7 g/dl) and a positive fecal occult blood test. Image studies
are unremarkable. Colonoscopy exam reveals numerous small pedunculated growths
involving entire colon. Image of biopsy of one of these growths are shown. What
is most likely the diagnosis for the patient?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Familial adenomatous polyposis
B. Gardner syndrome
C. Juvenile polyposis
D. Lynch syndrome
E. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
3. A 15-year-old boy presents with fatigue vague
abdominal pain for a year. He does not have diarrhea or constipation. He has
multiple family members in the paternal side with early onset colon cancers.
Physical exam is unremarkable except pale skin. No lymphadenopathy is noted.
Laboratory tests reveal a hemoglobin of 8.8 g/dl (normal 12.7-17.7 g/dl) and a
positive fecal occult blood test. Image studies are unremarkable. Colonoscopy
exam reveals numerous small pedunculated growths involving entire colon. Image
of biopsy of one of these growths are shown. Mutation of what gene is likely to
be associated with his condition?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. APC
B. C-kit
C. MSI
D. SMAD4
E. STK11
4. A 15-year-old boy presents with fatigue vague
abdominal pain for a year. He does not have diarrhea or constipation. He has
multiple family members in the paternal side with early onset colon cancers.
Physical exam is unremarkable except pale skin. No lymphadenopathy is noted.
Laboratory tests reveal a hemoglobin of 8.8 g/dl (normal 12.7-17.7 g/dl) and a
positive fecal occult blood test. Image studies are unremarkable. Colonoscopy
exam reveals numerous small pedunculated growths involving entire colon. Image
of biopsy of one of these growths are shown. What cellular function abnormality
is most likely associated with these findings?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Beta-catenin degradation
B. DNA mismatch repair
C. P53 degradation
D. Retinoblastoma 1 inactivation
E. Telomerase activation
5. Use this
case and image for the next four questions. A 37-year-old woman presents
with dull abdominal pain, abdominal distention, nausea, vomiting and bloody
stools for 3 months. She has a history of mandible osteoma 12 years ago that
was treated with surgery. She has a pack-year 30 history of cigarette smoking.
Her family history is significant for early onset colon cancer. The physical
examination reveals abdominal distention and a centrally located
intra-abdominal mass. Laboratory tests reveal a hemoglobin of 8.3 g/dl (normal
12-16 g/dl). Her white cells and platelets are within normal range. Peripheral
blood smear reveals no significant morphological abnormality. Fecal occult
blood test is positive. Abdominal ultrasound revealed a 12 cm mesentery mass. Biopsy
of the mass reveals benign appearing spindle cells. Per immunohistochemistry
studies, these spindle cells are positive for vimentin, but negative for
desmin, S100 and CD34. Proliferative index per ki67 is less than 1%. What test
should be performed next?
A. Bone marrow biopsy
B. Chest CT
C. Colonoscopy
D. Flow cytometry for peripheral blood
E. Serum iron analysis
6. A 37-year-old woman presents with dull abdominal
pain, abdominal distention, nausea, vomiting and bloody stools for 3 months. She
has a history of mandible osteoma 12 years ago that was treated with surgery.
She has a pack-year 30 history of cigarette smoking. Her family history is
significant for early onset colon cancer. The physical examination reveals
abdominal distention and a centrally located intra-abdominal mass. Laboratory
tests reveal a hemoglobin of 8.3 g/dl (normal 12-16 g/dl). Her white cells and
platelets are within normal range. Peripheral blood smear reveals no
significant morphological abnormality. Fecal occult blood test is positive. Abdominal
ultrasound revealed a 12 cm mesentery mass. Biopsy of the mass reveals benign
appearing spindle cells. Per immunohistochemistry studies, these spindle cells
are positive for vimentin, but negative for desmin, S100 and CD34.
Proliferative index per ki67 is less than 1%. Colonoscopic exam reveals
numerous polypoid growth in her transvers and descending colon. An image of her
biopsy is shown. What is the diagnosis for this polyp?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Hyperplastic polyp
B. Intramucosal adenocarcinoma
C. Peutz-Jegher polyp
D. Tubular adenoma
E. Villous adenoma
7. A 37-year-old woman presents with dull abdominal
pain, abdominal distention, nausea, vomiting and bloody stools for 3 months. She
has a history of mandible osteoma 12 years ago that was treated with surgery.
She has a pack-year 30 history of cigarette smoking. Her family history is
significant for early onset colon cancer. The physical examination reveals
abdominal distention and a centrally located intra-abdominal mass. Laboratory
tests reveal a hemoglobin of 8.3 g/dl (normal 12-16 g/dl). Her white cells and
platelets are within normal range. Peripheral blood smear reveals no
significant morphological abnormality. Fecal occult blood test is positive. Abdominal
ultrasound revealed a 12 cm mesentery mass. Biopsy of the mass reveals benign
appearing spindle cells. Per immunohistochemistry studies, these spindle cells
are positive for vimentin, but negative for desmin, S100 and CD34.
Proliferative index per ki67 is less than 1%. Colonoscopic exam reveals
numerous polypoid growth in her transvers and descending colon. An image of her
biopsy is shown. What is her condition?
A. Gardner syndrome
B. Inflammatory bowel disease
C. Juvenile polyposis
D. Lynch syndrome
E. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
8. A 37-year-old woman presents with dull abdominal
pain, abdominal distention, nausea, vomiting and bloody stools for 3 months. She
has a history of mandible osteoma 12 years ago that was treated with surgery.
She has a pack-year 30 history of cigarette smoking. Her family history is
significant for early onset colon cancer. The physical examination reveals
abdominal distention and a centrally located intra-abdominal mass. Laboratory
tests reveal a hemoglobin of 8.3 g/dl (normal 12-16 g/dl). Her white cells and
platelets are within normal range. Peripheral blood smear reveals no
significant morphological abnormality. Fecal occult blood test is positive. Abdominal
ultrasound revealed a 12 cm mesentery mass. Biopsy of the mass reveals benign
appearing spindle cells. Per immunohistochemistry studies, these spindle cells
are positive for vimentin, but negative for desmin, S100 and CD34. Proliferative
index per ki67 is less than 1%. Colonoscopic exam reveals numerous polypoid
growth in her transvers and descending colon. An image of her biopsy is shown.
Mutation of what gene is most likely associated with these findings?
A. APC
B. C-kit
C. MSI
D. SMAD4
E. STK11
9. Use this
case and image for the next four questions. A 45-year-old woman presents
with increased frequency of bowel movement for last 3 months. She was diagnosed
with FIGO I endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma 4 years ago that was
treated with total hysterectomy. Her past medical history is otherwise
unremarkable. Her family history is significant for colon and endometrial
cancers. Physical examination is unremarkable except rectal digital exam
finding of a firm mass at the posterior wall. Her routine laboratory tests are
within normal range. Radiologic examination reveals no evidence of
lymphadenopathy. No other abnormalities are noted. Colonoscopy exam reveals an
ulcerated mass approximately 3 cm above anal verge. The colon is otherwise
unremarkable. An image of the biopsy is shown. No squamous differentiation is
seen. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Kwz~commonswiki)
A. Metastatic endometrioid adenocarcinoma
B. Peutz-Jegher polyp
C. Primary rectal adenocarcinoma
D. Tubular adenoma
E. Villous adenoma
10. A 45-year-old woman presents with increased frequency
of bowel movement for last 3 months. She was diagnosed with FIGO I endometrial
endometrioid adenocarcinoma 4 years ago that was treated with total
hysterectomy. Her past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. Her family
history is significant for colon and endometrial cancers. Physical examination
is unremarkable except rectal digital exam finding of a firm mass at the
posterior wall. Her routine laboratory tests are within normal range.
Radiologic examination reveals no evidence of lymphadenopathy. No other
abnormalities are noted. Colonoscopy exam reveals an ulcerated mass
approximately 3 cm above anal verge. The colon is otherwise unremarkable. An
image of the biopsy is shown. No squamous differentiation is seen. Mutation of
what gene is most likely associated with her presentations?
(Image credit: Kwz~commonswiki)
A. APC
B. BRCA
C. MSIs
D. SMAD4
E. STK11
11. A 45-year-old woman presents with increased
frequency of bowel movement for last 3 months. She was diagnosed with FIGO I
endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma 4 years ago that was treated with total
hysterectomy. Her past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. Her family
history is significant for colon and endometrial cancers. Physical examination
is unremarkable except rectal digital exam finding of a firm mass at the
posterior wall. Her routine laboratory tests are within normal range.
Radiologic examination reveals no evidence of lymphadenopathy. No other
abnormalities are noted. Colonoscopy exam reveals an ulcerated mass
approximately 3 cm above anal verge. The colon is otherwise unremarkable. An
image of the biopsy is shown. No squamous differentiation is seen. Per
immunohistochemistry studies, these glandular cells are positive for MLH1, PMS2
but negative for MSH2 and MSH6. What is the diagnosis for her condition?
(Image credit: Kwz~commonswiki)
A. Cowden syndrome
B. Gardner syndrome
C. Juvenile polyposis
D. Lynch syndrome
E. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
12. A 45-year-old woman presents with increased
frequency of bowel movement for last 3 months. She was diagnosed with FIGO I
endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma 4 years ago that was treated with total
hysterectomy. Her past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. Her family
history is significant for colon and endometrial cancers. Physical examination
is unremarkable except rectal digital exam finding of a firm mass at the
posterior wall. Her routine laboratory tests are within normal range.
Radiologic examination reveals no evidence of lymphadenopathy. No other
abnormalities are noted. Colonoscopy exam reveals an ulcerated mass
approximately 3 cm above anal verge. The colon is otherwise unremarkable. An
image of the biopsy is shown. No squamous differentiation is seen. Per
immunohistochemistry studies, these glandular cells are positive for MLH1, PMS2
but negative for MSH2 and MSH6. What cellular function abnormality is most
likely associated with these findings?
(Image credit: Kwz~commonswiki)
A. Beta-catenin nuclear translocation
B. DNA mismatch repair
C. P53 degradation
D. Retinoblastoma 1 inactivation
E. Telomerase activation
13. Use this
image for this question. A 71-year-old man presents with fatigue and right
lower abdomen discomfort for 6 months. He denies other symptoms. His medical
history include squamous cell carcinoma of lung, chronic cholecystitis,
hypertension and type 2 diabetes. His family history is unremarkable. He has a
50 pack-year history of cigarette smoking. He drinks 2 cans of beer each day
since age 45. Physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory tests reveal a
hemoglobin of 11 g/dl (normal 13-18 g/dl). His white cell and platelets are within
normal ranges. Peripheral blood smear reveal no significant morphological
abnormality. Fecal occult blood test is positive. Colonoscopy exam reveals a
5.5 cm ulcerated mass at his cecum. Image of the biopsy is shown. What is the
diagnosis?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Juvenile polyp
B. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
C. Mucinous adenocarcinoma
D. Tubular adenoma
E. Villous adenoma
14. Use this case
and this image for the next two questions. A 65-year-old man presents with
progressive right lower abdomen pain. She has a history of adenocarcinoma of
left lung at age of 56 and was treated with surgery and chemotherapy. Her past
medical history is otherwise unremarkable. Physical examination reveals no
significant abnormalities. CBC reveals a hemoglobin of 7.5 g/dl (normal 12-16
g/dl), MCV of 75 fl (normal 85-95 fl) and red cell distribution width of 18%
(normal 13-15%). Additional laboratory tests results including iron of 23
mcg/dl (normal 50-150 mcg/dl) and UIBC of 410 mcg/dl (normal 200-305 mcg/dl). Fecal
occult blood test is positive. What is the next step of management?
A. Bone marrow biopsy
B. Colonoscopy
C. Folate supplementation
D. Iron supplementation
E. Peripheral blood flow cytometry
15. A 65-year-old man presents with progressive right
lower abdomen pain. She has a history of adenocarcinoma of left lung at age of
56 and was treated with surgery and chemotherapy. Her past medical history is
otherwise unremarkable. Physical examination reveals no significant
abnormalities. CBC reveals a hemoglobin of 7.5 g/dl (normal 12-16 g/dl), MCV of
75 fl (normal 85-95 fl) and red cell distribution width of 18% (normal 13-15%).
Additional laboratory tests results including iron of 23 mcg/dl (normal 50-150
mcg/dl) and UIBC of 410 mcg/dl (normal 200-305 mcg/dl). Fecal occult blood test
is positive. Colonoscopy examination reveals a 2.4 cm mass at his ascending
colon. An image of the biopsy is shown. Per immunohistochemistry studies, these
cells are negative for TTF1. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Patho [CC BY-SA 3.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Adenocarcinoma, NOS
B. Carcinoid
C. Hyperplastic polyp
D. Metastatic pulmonary adenocarcinoma
E. Signet ring cell carcinoma
16. Use this
image for this question. A 35-year-old man presents with worsening epigastric
pain and a 20 pound weight loss in the last 6 months. He has a history of
reflux gastritis for 5 years and ulcerative colitis for 13 years. His medical
history is otherwise unremarkable. Physical examination and routine laboratory
tests reveal no significant abnormalities. Colonoscopy exam reveal diffuse
erythematous changes with many polypoid growths involving transverse and sigmoid
colon. A 2.5 cm transverse colon polyp has focal surface ulceration. An image
of a biopsy of this polyp is shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Adenocarcinoma, NOS
B. Hyperplastic polyp
C. Inflammatory polyp
D. Juvenile polyp
E. Mucinous adenocarcinoma
17. Use this case
and this image for the next two questions. A 49-year-old homosexual man
presents with anal pain for 3 months. He denies other symptoms. He is HIV
positive since age 30, and has history of syphilic chancre at age 23, that was
treated with penicillin, and multiple episodes of genital herpes and condyloma.
Rectal digital exam reveals a firm mass 2 cm above verge. His laboratory tests
reveals a CD4+ T cell count of 350/mcl (normal 500-1500/mcl). No other
abnormalities are noted. An image of the biopsy is shown. Per
immunohistochemistry studies, these cells are positive for cytokeratin, and
negative for CD20, CD45, S100 and chromogranin. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: LWozniak&KWZielinski [CC BY-SA
3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Condyloma
B. Melanoma
C. Small cell carcinoma
D. Small lymphocytic lymphoma
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
18. A 49-year-old homosexual man presents with anal
pain for 3 months. He denies other symptoms. He is HIV positive since age 30,
and has history of syphilic chancre at age 23, that was treated with
penicillin, and multiple episodes of genital herpes and condyloma. Rectal
digital exam reveals a firm mass 2 cm above verge. His laboratory tests reveals
a CD4+ T cell count of 350/mcl (normal 500-1500/mcl). No other abnormalities
are noted. An image of the biopsy is shown. Per immunohistochemistry studies,
these cells are positive for cytokeratin, and negative for CD20, CD45, S100 and
chromogranin. What is most likely associated with this lesion?
(Image credit: LWozniak&KWZielinski [CC BY-SA
3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. EB virus
B. Human herpes virus 2
C. Human immunodeficiency virus
D. Human papilloma virus
E. Treponema pallidum
19. Use this
image for this question. A 29-year-old woman presents with recurrent right
abdomen dull pain for 6 months. She has a history of dysmenorrhea since age 21.
Her past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. Physical examination reveals
tenderness at right lower abdomen without rebound tenderness or guarding. No
other abnormalities are noted. Laboratory test results are within normal range.
Abdominal CT reveals enlarged appendix. Appendectomy was performed and a 0.5 cm
pale area is noted at the tip. Image of the microscopic exam is shown. Per
immunohistochemistry studies, these cells are positive for cytokeratin and chromogranin.
What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Sarahkayb [CC BY-SA 4.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)])
A. Adenocarcinoma
B. Carcinoid
C. Chronic appendicitis
D. Endometriosis
E. Small cell carcinoma
20. A 45-year-old woman presents with vague lower
abdominal pain for 6 months. Her past medical history is unremarkable. Physical
examination reveals tenderness at left and right lower abdominal without rebound
tenderness or guarding. Her laboratory test results are within normal ranges.
Image studies reveals a dilated appendix, and multiple small masses up to 1.5
cm on the serosa side of her uterus and rectum. Laparotomy was performed.
Gelatinous material are seen attached to appendix, and uterus, rectum and
parietal peritoneum. Microscopic examination of the appendix reveal a cystic
dilation lined by columnar cells with abundant pale cytoplasm. Focally there
are signs of perforation. No cytological atypia are seen. What is most likely
the diagnosis?
A. Carcinoid
B. Mucinous adenocarcinoma
C. Ovarian borderline mucinous neoplasm
D. Peritoneal carcinomatosis
E. Pseudomyxoma peritonei
Back to intestinal
tumors
Back to contents







Comments
Post a Comment