Practice questions Esophageal pathology
Practice questions
Esophageal pathology
Updated: 02/28/2019
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
1. Use this case for the next two questions. A 35-year-old woman
presents with intermittent dysphagia and chest pain for 1 year. The pain is triggered by
swallowing large amount of water. It is a sharp pain in the lower substernal
area. She denies other symptoms. She has a history of type 2 diabetes but
denies any cardiovascular system disorders. She does not smoke cigarette nor
drink alcohol. Physical examination reveals no significant abnormalities. Laboratory
tests are within normal range. Upper endoscopic exam, 24 hour esophageal impedance-pH
monitoring and barium esophagogram reveal no esophageal or stomach
abnormalities. What test is appropriate next?
A. Coronary angiogram
B. EKG
C. Esophageal biopsy
D. High-resolution
manometry
E. Sonographic exam for
mediastinal abnormalities
2. A 35-year-old woman presents with intermittent dysphagia and chest pain for 1 year. The
pain is triggered by swallowing large amount of water. It is a sharp pain in
the lower substernal area. She denies other symptoms. She has a history of type
2 diabetes but denies any cardiovascular system disorders. She does not smoke
cigarette nor drink alcohol. Physical examination reveals no significant
abnormalities. Laboratory tests are within normal range. Upper endoscopic exam,
24 hour esophageal impedance-pH monitoring and barium esophagogram reveal no
esophageal or stomach abnormalities.
High-resolution manometry
reveals simultaneously increased intraesophageal pressure of the entire
distal esophagus, following swallowing large amount of water. What is the diagnosis?
A. Achalasia
B. Candidiasis
C. Diffuse esophageal spasm
D. Esophageal web
E. Reflux esophagitis
3. Use this case for the next
two questions.
A 65-year-old man presents with dysphagia
and regurgitation for 3 years. His past medical history is unremarkable.
Physical examination and laboratory tests are unremarkable. Upper endoscopic examination
reveals dilated distal third esophagus and a stricture near gastro-esophageal
junction. No significant mucosal abnormalities are noted. Barium esophagogram reveals
dilatation of mid to distal esophagus and a stenosis at gastroesophageal
junction. What is most likely the diagnosis?
A. Achalasia
B. Barret esophagus
C. Diffuse esophageal spasm
D. Esophageal web
E. Reflux esophagitis
4. A 65-year-old man presents with dysphagia and regurgitation
for 3 years. His past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination and
laboratory tests are unremarkable. Upper endoscopic examination reveals dilated
distal third esophagus and a stricture near gastro-esophageal junction. No
significant mucosal abnormalities are noted. Barium esophagogram reveals
dilatation of mid to distal esophagus and a stenosis at gastroesophageal
junction. What is most likely causing his presentations?
A. Distal esophagus scarring
B. Esophageal glandular proliferation
C. Esophageal mucosal protrusions
D. Muscularis propria hypertrophy
E. Squamous cell proliferation
5. A 44-year-old man presents with intermittent dysphagia
for 3 months. He denies abdominal pain and other constitutional symptoms. His
past medical history and physical examination are unremarkable. Laboratory
tests reveals a hemoglobin of 9.5 g/dl (normal 13.5-17.5 g/dl), MCV 72 fL (normal
80-95 fL) and serum iron of 35 microgram/dl (normal 50-150 microgram/dl). The
white cells and platelets are unremarkable. Barium esophagogram reveals an
irregular filling defect at distal esophagus. Upper endoscopic examination reveals
a constricting concentric thickening of esophageal wall with focal mucosal ulceration.
Biopsy reveals squamous mucosa with reactive changes. What is the diagnosis?
A. Achalasia
B. Adenocarcinoma
C. Esophagus ring
D. Esophagus web
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
6. A 75-year-old woman presents with vomiting followed
by epigastric pain, hematemesis and syncope. She has history of type 2 diabetes
and deep vein thrombosis and is current taking Coumadin. Physical examination
reveals pale skin with a blood pressure of 85/50 mmHg and heart rate of 110
bpm. Laboratory tests reveals a hemoglobin of 7.4 g/dl (normal 12-16 g/dl), INR
of 2.5 (target range: 2-3). All three lineages are morphologically
unremarkable. Upper endoscopy reveals a longitudinal fissure along the gastroesophageal
junction. What is the diagnosis?
A. Barrett esophagus
B. Candidiasis
C. Mallory Weiss tear
D. Reflux esophagitis and ulcer
E. Varices
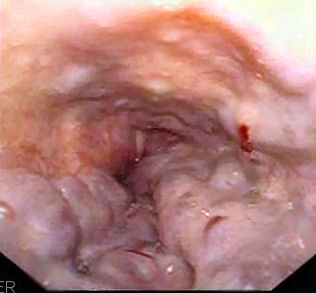
7. Use this
image for this question. A 55-year-old woman presents
with hematemesis for 1 hour. She has a history of alcoholic cirrhosis, type 2
diabetes, and Barrett esophagus. Physical examination reveals pale skin, with a
blood pressure of 82/45 mmHg and a heart rate of 130 bpm. Laboratory tests
reveal a hemoglobin of 7.5 g/dl (normal 12-16 g/dl), AST of 51U/L (normal 10-34
U/L). His renal function tests, white cells and platelets are within normal
range. Upper endoscope examination reveals findings as shown in the image. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Samir)
A. Adenocarcinoma
B. Candidiasis
C. Esophageal web
D. Mallory Weiss tear
E. Varices
8. Use this
image for this question A
31-year-old man presents with dysphagia, odynophagia and retrosternal chest
pain for a day. The pain is triggered by any type of food intake. His past
medical history is unremarkable. She denies any constitutional symptoms. Physical examination and laboratory tests are
unremarkable. Upper endoscopic exam reveal multiple shallow ulcers in a
background erythematous mucosa, at distal esophagus. No discrete mass is seen. Cytological
examination of these ulcers reveal findings shown in the image. What is the
diagnosis?
(Image credit CDC/ Dr. Edwin P. Ewing, Jr. )
A. Adenocarcinoma
B. Candidiasis
C. Eosinophilic esophagitis
D. Herpes esophagitis
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
9. A 49-year-old woman presents with progressive
dysphagia and odynophagia for 3 months. She has type 2 diabetes. She has a 30
pack-year history of cigarette smoking and is a social drinker. Physical examination
and laboratory tests are unremarkable. Upper endoscopic examination reveals
irregular pale to white plaques at distal esophagus. Small ulceration is seen.
Biopsy of these lesions reveal hyperplastic squamous epithelium with neutrophilic
infiltration. No viral inclusion is seen. Special stain reveal fungal hyphae
within the epithelium. What is the diagnosis?
A. Adenocarcinoma
B. Candidiasis
C. Eosinophilic esophagitis
D. Herpes esophagitis
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
10. Use this case for the next
two questions.
A 24-year-old man presents with
dysphagia, nausea and substernal pain for 3 days. He denies other symptoms. He
has history of atopic dermatitis before age of 2. He does not smoke cigarette
nor drink alcohol. Physical examination and laboratory tests are within normal
range. Upper endoscopy reveals white plaques at distal esophagus. Biopsy reveals
squamous mucosa with mild squamous hyperplasia and numerous intraepithelial eosinophils.
No cytological atypia is seen. Special stain reveals no fungal hyphae. What is
the diagnosis?
A. Adenocarcinoma
B. Candidiasis
C. Eosinophilic esophagitis
D. Herpes esophagitis
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
11. A 24-year-old man presents with dysphagia, nausea and
substernal pain for 3 days. He denies other symptoms. He has history of atopic
dermatitis before age of 2. He does not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol. Physical
examination and laboratory tests are within normal range. Upper endoscopy
reveals white plaques at distal esophagus. Biopsy reveals squamous mucosa with
mild squamous hyperplasia and numerous intraepithelial eosinophils. No
cytological atypia is seen. Special stain reveals no fungal hyphae. What is causing
these findings?
A. Allergic reaction
B. Bacterial infection
C. Herpes infection
D. Monoclonal eosinophilic proliferation
E. Parasite infection
12. A 49-year-old man presents with intermittent dysphagia,
heartburn and vomiting for 6 months. He drinks a bottle of whiskey a day for 20
years, and has a 30 pack year history of cigarette smoking. Physical
examination is unremarkable. Laboratory tests reveals normal CBC and mildly
elevated AST. Upper endoscopy examination reveals irregular white patches at
distal esophagus. Biopsy of these patches reveals slightly hyperplastic squamous
epithelium with diffuse eosinophilic infiltrate. No glandular components are
seen. Ambulatory pH monitoring reveals periodically reduced pH, that is
compatible with his symptoms. What is likely causing his clinical
presentations?
A. Allergic reaction
B. Candida infection
C. Gastric and intestinal metaplasia of distal squamous
mucosa
D. Reflux of gastric contents
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
13. Use this case for the next
two questions.
A 51-year-old man presents with worsening
dysphagia and heartburn for 1 week. He has a history of reflux esophagitis for
10 years, and type 2 diabetes for 5 years. Physical examination and laboratory
tests are within normal ranges. Gastroscopic examination reveals a few
irregular erythematous patches at distal esophagus. No discrete tumor or ulcer
is seen. Biopsy reveal mixed squamous and gastric mucosa with mild
lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Focally there are slightly large cells with pale
to gray cytoplasm and small basally located nuclei. Most of the glandular cells
have pale pink cytoplasms. No significant architectural or cytological atypia
is noted. What is the diagnosis?
A. Adenocarcinoma
B. Barrett esophagus
C. Candidiasis
D. Lymphocytic esophagitis
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
14. A 51-year-old man presents with worsening dysphagia
and heartburn for 1 week. He has a history of reflux esophagitis for 10 years, and
type 2 diabetes for 5 years. Physical examination and laboratory tests are
within normal ranges. Gastroscopic examination reveals a few irregular erythematous
patches at distal esophagus. No discrete tumor or ulcer is seen. Biopsy reveal
mixed squamous and gastric mucosa with mild lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate.
Focally there are slightly large cells with pale to gray cytoplasm and small
basally located nuclei. Most of the glandular cells have pale pink cytoplasms.
No significant architectural or cytological atypia is noted. What risk is elevated
for this patient?
A. Achalasia
B. Adenocarcinoma
C. Esophageal web
D. Massive hemorrhage
E. Metastasis
15. Use this case for the next
two questions.
A 55-year-old man presents with
progressive dysphagia, vomiting and a 20 pound weight loss from 2 months. He has
a history of diabetes, helicobacter gastritis, reflux esophagitis, Barrett
esophagus, and low grade prostate adenocarcinoma treated with surgery. He
smokes cigarette one and a half pack a day for 30 years and is a social
drinker. Physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory tests reveal a
hemoglobin of 8 g/dl (normal 13.5-17.5 g/dl). No other abnormality is noted. Barium
esophagogram reveals irregular filling defects at distal esophagus. Endoscopy
examination reveals irregularly raised area with whitish surface occupying approximately
60% of the circumferences. Biopsy of these lesions reveal mixed squamous and
gastric type mucosa. Slightly enlarged columnar cells with greyish cytoplasm
and basally located small nuclei are seen. Focally there are irregular glands
lined by moderately atypical cells in the lamina propria. The squamous
epithelium has scattered neutrophilic and eosinophilic infiltrate. No
significant keratinocytic atypia is noted. What is most likely the diagnosis?
A. Adenocarcinoma
B. Candida esophagitis
C. Esophageal web
D. Metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
16. A 55-year-old man presents with progressive dysphagia,
vomiting and a 20 pound weight loss from 2 months. He has a history of diabetes,
helicobacter gastritis, reflux esophagitis, Barrett esophagus, and low grade
prostate adenocarcinoma treated with surgery. He smokes cigarette one and a
half pack a day for 30 years and is a social drinker. Physical examination is unremarkable.
Laboratory tests reveal a hemoglobin of 8 g/dl (normal 13.5-17.5 g/dl). No other
abnormality is noted. Barium esophagogram reveals irregular filling defects at
distal esophagus. Endoscopy examination reveals irregularly raised area with
whitish surface occupying approximately 60% of the circumferences. Biopsy of
these lesions reveal mixed squamous and gastric type mucosa. Slightly enlarged
columnar cells with greyish cytoplasm and basally located small nuclei are
seen. Focally there are irregular glands lined by moderately atypical cells in the
lamina propria. The squamous epithelium has scattered neutrophilic and eosinophilic
infiltrate. No significant keratinocytic atypia is noted. What in his history
is most likely associated with his current findings?
A. Barrett esophagus
B. Cigarette smoking
C. Diabetes
D. Helicobacter gastritis
E. Prostate adenocarcinoma
17. Use this case for the next
two questions.
A 79-year-old man presents with
progressive dysphagia and a 10 pound weight loss in a month. His medical
history including esophagus web, Barrett esophagus, type 2 diabetes and
hypertension. He has a 50 pack year history of cigarette smoking and has been
drinking wines 2-3 glasses per day for 40 years. Physical examination and laboratory
tests are unremarkable. Barium esophagogram reveal irregular filling defect at the
mid portion of his esophagus. Upper endoscopy examination reveals a 4.4 cm wide
based lesion with surface ulceration. Biopsy reveals irregular nest of cells as
shown in the image. What is the diagnosis?
(Image source: The Armed Forces Institute of Pathology
(AFIP))
A. Adenocarcinoma
B. Candida esophagitis
C. Eosinophilic esophagitis
D. Esophageal web
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
18. A 79-year-old man presents with progressive
dysphagia and a 10 pound weight loss in a month. His medical history including
esophagus web, Barrett esophagus, type 2 diabetes and hypertension. He has a 50
pack year history of cigarette smoking and has been drinking wines 2-3 glasses
per day for 40 years. Physical examination and laboratory tests are
unremarkable. Barium esophagogram reveal irregular filling defect at the mid
portion of his esophagus. Upper endoscopy examination reveals a 4.4 cm wide
based lesion with surface ulceration. Biopsy reveals irregular nest of cells as
shown in the image. What in his history is most likely associated with these findings?
(Image source: The Armed Forces Institute of Pathology
(AFIP))
A. Barrett esophagus
B. Cigarette smoking
C. Diabetes
D. Esophagus web
E. Hypertension
Back to esophagus
pathology
Back to contents



Comments
Post a Comment