Practice questions A, intestinal tumors
Practice questions A, intestinal tumors
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
1. Use this
case and this image for the next three questions. A 68-year-old woman
presents with fatigue for 3 months. She has type 2 diabetes, obesity and Graves
disease. She smokes cigarette 1 pack a day for 15 years, and is a social
drinker. Her family history is significant for multiple female relatives with
endometrial and breast cancers. Physical examination reveals no significant
findings except slightly pale conjunctiva and a BMI of 31 (normal 18.5-24.9).
Laboratory test reveals a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal 12 – 15 g/dl), red
cell distribution width (RDW) of 16% (normal 13-15), and serum ferritin of 16
mcg/l (normal 18-160 mcg/l). Her white cells, platelets, PT and aPTT are within
normal range. Peripheral blood smears reveal no significant morphological
abnormalities nor immature cells. Image studies are unremarkable. What is a
proper test for diagnosis?
A. Colonoscopy
B. Genetic counseling
C. Hemoglobin electrophoresis
D. Lymphocytes phenotyping
E. Platelet function tests
2. A 68-year-old woman presents with fatigue for 3
months. She has type 2 diabetes, obesity and Graves disease. She smokes
cigarette 1 pack a day for 15 years, and is a social drinker. Her family
history is significant for multiple female relatives with endometrial and
breast cancers. Physical examination reveals no significant findings except
slightly pale conjunctiva and a BMI of 31 (normal 18.5-24.9). Laboratory test
reveals a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal 12 – 15 g/dl), red cell distribution
width (RDW) of 16% (normal 13-15), and serum ferritin of 16 mcg/l (normal
18-160 mcg/l). Her white cells, platelets, PT and aPTT are within normal range.
Peripheral blood smears reveal no significant morphological abnormalities nor
immature cells. Image studies are unremarkable.
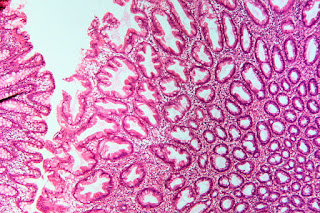
Colonoscopy examination reveal a 1.5 cm pedunculated
polyp with focal ulceration at her splenic flexure. Polypectomy was performed
and the microscopic findings are shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Patho [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Adenocarcinoma
B. Hyperplastic polyp
C. Juvenile polyp
D. Sessile serrated adenoma
E. Tubular adenoma
3. A 68-year-old woman presents with fatigue for 3
months. She has type 2 diabetes, obesity and Graves disease. She smokes
cigarette 1 pack a day for 15 years, and is a social drinker. Her family
history is significant for multiple female relatives with endometrial and
breast cancers. Physical examination reveals no significant findings except
slightly pale conjunctiva and a BMI of 31 (normal 18.5-24.9). Laboratory test
reveals a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal 12 – 15 g/dl), red cell distribution
width (RDW) of 16% (normal 13-15), and serum ferritin of 16 mcg/l (normal
18-160 mcg/l). Her white cells, platelets, PT and aPTT are within normal range.
Peripheral blood smears reveal no significant morphological abnormalities nor
immature cells. Image studies are unremarkable. Colonoscopy examination reveal
a 1.5 cm pedunculated polyp with focal ulceration at her splenic flexure.
Polypectomy was performed and the microscopic findings are shown. What is most
likely the cause of these findings?
(Image credit: Patho [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Activating mutation of beta catenin
B. Chronic inflammation
C. Delayed shedding of surface epithelial cells
D. Hypermethylation of CpG island
E. Microsatellite instability
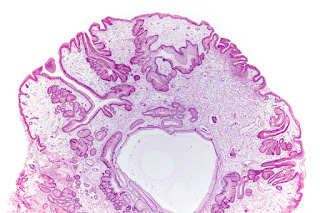
4. Use this
image for this questions. A 39-year-old woman presents with worsening
fatigue for two months. She has a history of ulcerative colitis for 8 years.
Physical examination is unremarkable. Her laboratory tests reveal a hemoglobin
of 7.5 g/dl (normal 12-15 g/dl) and mcv of 72 fl (normal 80-96 fl). Other
routine tests are within normal range. Colonoscopy examination reveals diffuse
mild to moderate inflammatory changes and a few polypoid growths up to 1.2 cm
in greatest dimension. Image of the biopsy is shown. No significant atypia is
noted. What is the diagnosis concerning the polyp biopsied?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC
BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Hyperplastic polyp
B. Inflammatory polyp
C. Intramucosal adenocarcinoma
D. Sessile serrated adenoma
E. Tubular adenoma
5. Use this
case and this image for the next two questions. A 2-year-old boy presents
with melena for 3 months. His past medical history is unremarkable. Physical
examination reveals pale conjunctiva and both weight and heights at 15th
percentile. No skin or mucosal pigmentation is noted. Laboratory tests reveals
a hemoglobin at 5.5 g/dl (normal 10.5-14.5 g/dl). Blood smear reveals no
morphological abnormalities. Upper endoscopic examination reveals a few
ulcerated bleeding gastric polyps. Colonoscopy examination reveals multiple
pedunculated polyps in his colon. Microscopically, the colon polyps have same
morphology. Image of the gastric polyp is shown. What is most likely the
diagnosis?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Hyperplastic polyps
B. Inflammatory polyps
C. Juvenile polyposis
D. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
E. Sessile serrated adenoma
6. A 2-year-old boy presents with melena for 3 months.
His past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals pale
conjunctiva and both weight and heights at 15th percentile. No skin
or mucosal pigmentation is noted. Laboratory tests reveals a hemoglobin at 5.5
g/dl (normal 10.5-14.5 g/dl). Blood smear reveals no morphological
abnormalities. Upper endoscopic examination reveals a few ulcerated bleeding
gastric polyps. Colonoscopy examination reveals multiple pedunculated polyps in
his colon. Microscopically, the colon polyps have same morphology. Image of the
gastric polyp is shown. Mutation of what gene is most likely associated with
these findings?
A. APC
B. Beta-catenin
C. MYH
D. SMAD4
E. STK11
7. Use this
case and this image for the next two questions. A 38-year-old man presents with
intermittent melena for 2 months. He does not have diarrhea, constipation or
abdominal pain. His past medical history is unremarkable. He has a few family
members with lung, colon and breast cancers. He does not smoke cigarette nor
drink alcohol. Physical examination reveals a few irregular brown macules at
his lips, conjunctiva, chest and back. Laboratory tests are unremarkable except
positive fecal occult blood test. Image studies reveals multiple masses in his
colon. Colonoscopy exam reveals masses up to 2.5 cm in greatest dimension in his
ascending and sigmoid colon. Some of theses masses are ulcerated. An image of
the biopsy is shown. No cytological atypia is noted. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Hyperplastic polyps
B. Inflammatory polyps
C. Juvenile polyposis
D. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
E. Sessile serrated adenoma
8. A 38-year-old man presents with intermittent melena
for 2 months. He does not have diarrhea, constipation or abdominal pain. His
past medical history is unremarkable. He has a few family members with lung,
colon and breast cancers. He does not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol.
Physical examination reveals a few irregular brown macules at his lips,
conjunctiva, chest and back. Laboratory tests are unremarkable except positive
fecal occult blood test. Image studies reveals multiple masses in his colon.
Colonoscopy exam reveals masses up to 2.5 cm in greatest dimension in his
ascending and sigmoid colon. Some of theses masses are ulcerated. An image of
the biopsy is shown. No cytological atypia is noted. Mutation of what gene is
most likely associated with these findings?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. APC
B. Beta-catenin
C. MYH
D. SMAD4
E. STK11
9. Use this
image for this question. A 65-year-old woman presents for screening
colonoscopy exam. She denies symptoms of diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain
or weight loss. She has adenocarcinoma of lung diagnosed two years ago that was
treated with surgery and chemotherapy. She also has type 2 diabetes,
hypertension and hypothyroidism. She denies cigarette or alcohol usage.
Physical examination is unremarkable. Colonoscopy examination reveals a single
pedunculated polyp at her cecum. An image is shown. No significant cytological
atypia is noted. What is the diagnosis?
Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)]
A. Hyperplastic polyp
B. Sessile serrated adenoma
C. Tubular adenoma
D. Tubulovillous adenoma
E. Villous adenoma
10. Use this image
for this question. A
59-year-old man presents with fatigue for 3 months. He does not have other
symptoms. His past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination
reveals slightly pale skin. Laboratory tests reveal a hemoglobin of 11.2 g/dl
(normal 13-18 g/dl). Fecal occult blood test is positive. Image studies reveal
a 2 cm mass at his transverse colon. Colonoscopy exam reveals a polypoid growth
with wide base and a cauliflower like surface. No ulcer is noted. Image of the
biopsy is shown. No significant cytological atypia is noted. What is the
diagnosis?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Hyperplastic polyp
B. Sessile serrated adenoma
C. Tubular adenoma
D. Tubulovillous adenoma
E. Villous adenoma
11. Use this image
for this question. A 66-year-old woman presents with fatigue for
3 months. She does not have diarrhea, constipation, or weight loss. Her past
medical history including FIGO I endometrial adenocarcinoma. Physical
examination reveals slightly pale skin. Laboratory tests reveal a hemoglobin of
9.6 g/dl (normal 13-18 g/dl). Fecal occult blood test is positive. Colonoscopy
exam reveals a polypoid growth with wide base and a focally ulcerated
cauliflower like surface. Image of the biopsy is shown. No significant
cytological atypia is noted. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Nephron
[CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Metastatic endometrial adenocarcinoma
B. Sessile serrated adenoma
C. Tubular adenoma
D. Tubulovillous adenoma
E. Villous adenoma
12. Use this
case and this image for the next two questions. A 77-year-old man presents with fatigue and vague
left lower abdominal discomfort. He has a history of hypertension, type 2
diabetes and prostate adenocarcinoma. His family history is significant for
multiple members with colon and lung cancers. Laboratory tests results,
including PSA, are within normal range. Colonoscopy exam reveals a 2.5 cm flat
growth with a cauliflower appearing surface at his sigmoid colon. No ulcer nor
hemorrhage is noted. An image of the biopsy is shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma
B. Sessile serrated adenoma
C. Tubular adenoma
D. Tubulovillous adenoma
E. Villous adenoma
13. A 77-year-old man presents with fatigue and vague left
lower abdominal discomfort. He has a history of hypertension, type 2 diabetes
and prostate adenocarcinoma. His family history is significant for multiple
members with colon and lung cancers. Laboratory tests results, including PSA,
are within normal range. Colonoscopy exam reveals a 2.5 cm flat growth with a
cauliflower appearing surface at his sigmoid colon. No ulcer nor hemorrhage is
noted. An image of the biopsy is shown. Mutation of what gene is likely
associated with these changes?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Androgen receptor
B. Beta-catenin
C. MSI
D. SMAD4
E. STK11
14. Use this
case and this image for the next two questions. A 66-year-old woman presents with fatigue for
3 months. She does not have diarrhea, constipation, or weight loss. Her past
medical history and physical examination are unremarkable. Laboratory tests
reveal a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal 12-15 g/dl). Fecal occult blood test is
positive. No other abnormalities are noted. Colonoscopy exam reveals a 1.5 cm
pedunculated growth with smooth surface at her sigmoid colon. The growth is
removed. Majority of the growth is composed of tubular glands lined by cells
with basally located crowded elongated hyperchromic nuclei. At a small focus
there are glands as shown. These glands are only seen in the mucosa and does
not involve the margin. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Nephron
[CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)]))
A. Intramucosal adenocarcinoma
A. Intramucosal adenocarcinoma
B. Mucinous adenocarcinoma
C. Sessile serrated adenoma
D. Tubular adenoma
E. Villous adenoma
15. A 66-year-old
woman presents with fatigue for 3 months. She does not have diarrhea,
constipation, or weight loss. Her past medical history and physical examination
are unremarkable. Laboratory tests reveal a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal
12-15 g/dl). Fecal occult blood test is positive. No other abnormalities are
noted. Colonoscopy exam reveals a 1.5 cm pedunculated growth with smooth
surface at her sigmoid colon. The growth is removed. Majority of the growth is
composed of tubular glands lined by cells with basally located crowded
elongated hyperchromic nuclei. At a small focus there are glands as shown.
These glands are only seen in the mucosa and do not involve the margin. How
is the patient need to be treated?
(Image credit: Nephron
[CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)]))
A. Chemotherapy
B. Colectomy
C. Mucosal resection
with lymph node dissection
D. No additional
treatment
E. Radiation therapy
16.
Use this
case and this image for the next three questions. A 39-year-old man presents with fatigue for 6
months. He has a history of type 1 diabetes, obesity and major depression. He
denies other symptoms, including night sweating, nausea and weight loss. His
family history is remarkable for a few family members in the paternal side who
were diagnosed with colon or rectal cancer from age 40 to 55. He has a 10 pack
year history of cigarette smoking, but denies usage of alcohol or illicit drugs.
Physical examination reveals no significant findings except a body weight of
280 pounds. His laboratory findings are within normal ranges, except a
hemoglobin of 10.8 g/dl (14-18 g/dL) and elevated blood lipid levels including
a total cholesterol of 320 mg/dL (125-200 mg/dL). Colonoscopic exam reveals approximately
30 polyps, up to 0.7 cm in greatest dimension, scattered in his ascending and
transverse colon. An image of microscopic examination of these polyps are
shown. Molecular tests of what genes are most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
(Image
Credit: Nephron, CC BY-SA 3.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
A.
APC and MUTYH
B. BMPR1A and SMAD4
C. Microsatellite-instability mutations and CpG methylation
D. PTEN and STK11
E. TSC1 and TSC2
B. BMPR1A and SMAD4
C. Microsatellite-instability mutations and CpG methylation
D. PTEN and STK11
E. TSC1 and TSC2
17.
A 39-year-old man presents with fatigue for 6 months. He has a history of type
1 diabetes, obesity and major depression. He denies other symptoms, including
night sweating, nausea and weight loss. His family history is remarkable for a
few family members in the paternal side who were diagnosed with colon or rectal
cancer from age 40 to 55. He has a 10 pack year history of cigarette smoking,
but denies usage of alcohol or illicit drugs. Physical examination reveals no
significant findings except a body weight of 280 pounds. His laboratory
findings are within normal ranges, except a hemoglobin of 10.8 g/dl (14-18
g/dL) and elevated blood lipid levels including a total cholesterol of 320 mg/dL
(125-200 mg/dL). Colonoscopic exam reveals approximately 30 polyps, up to 0.7 cm
in greatest dimension, scattered in his ascending and transverse colon. An
image of microscopic examination of these polyps are shown. Mutation of what
gene is most likely seen in this patient?


(Image
Credit: Nephron, CC BY-SA 3.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
A. APC
B. BMPR1A
C. MUTYH
D. SMAD4
E. STK11
18. A 39-year-old man presents with fatigue for 6 months. He has a history of type 1 diabetes, obesity and major depression. He denies other symptoms, including night sweating, nausea and weight loss. His family history is remarkable for a few family members in the paternal side who were diagnosed with colon or rectal cancer from age 40 to 55. He has a 10 pack year history of cigarette smoking, but denies usage of alcohol or illicit drugs. Physical examination reveals no significant findings except a body weight of 280 pounds. His laboratory findings are within normal ranges, except a hemoglobin of 10.8 g/dl (14-18 g/dL) and elevated blood lipid levels including a total cholesterol of 320 mg/dL (125-200 mg/dL). Colonoscopic exam reveals approximately 30 polyps, up to 0.7 cm in greatest dimension, scattered in his ascending and transverse colon. An image of microscopic examination of these polyps are shown. What type of polyp this is?

(Image Credit: Nephron, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
A. Hyperplastic polyp
B. Inflammatory polyp
C. Sessile serrated adenoma
D. Tubular adenoma
E. Villous adenoma
A. APC
B. BMPR1A
C. MUTYH
D. SMAD4
E. STK11
18. A 39-year-old man presents with fatigue for 6 months. He has a history of type 1 diabetes, obesity and major depression. He denies other symptoms, including night sweating, nausea and weight loss. His family history is remarkable for a few family members in the paternal side who were diagnosed with colon or rectal cancer from age 40 to 55. He has a 10 pack year history of cigarette smoking, but denies usage of alcohol or illicit drugs. Physical examination reveals no significant findings except a body weight of 280 pounds. His laboratory findings are within normal ranges, except a hemoglobin of 10.8 g/dl (14-18 g/dL) and elevated blood lipid levels including a total cholesterol of 320 mg/dL (125-200 mg/dL). Colonoscopic exam reveals approximately 30 polyps, up to 0.7 cm in greatest dimension, scattered in his ascending and transverse colon. An image of microscopic examination of these polyps are shown. What type of polyp this is?

(Image Credit: Nephron, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
A. Hyperplastic polyp
B. Inflammatory polyp
C. Sessile serrated adenoma
D. Tubular adenoma
E. Villous adenoma
Back to intestinal
tumors
Back to contents







Comments
Post a Comment