Practice questions, skin tumors 2
Practice
questions, skin tumors 2
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
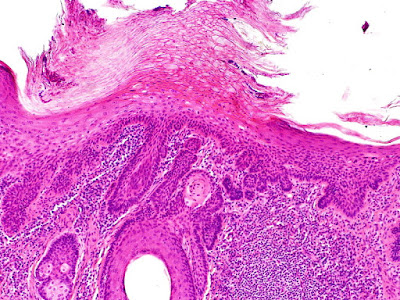
1. Use this case
and this image for the next two questions. A 65-year-old male farmer
presents with an incidentally found slightly discolored skin lesion on his
forehead. He denies other symptoms. He has a history of multiple squamous cell
carcinomas and basal cell carcinomas of skin, all treated with local
resections. Physical examination reveals a 2.5 cm slightly erythematous area
with a rough surface at his left forehead. No other significant abnormalities
are noted. An image of the biopsy is shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image: LWozniak&KWZielinski [CC BY-SA 3.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Actinic keratosis
B. Basal cell carcinoma
C. Bowen disease
D. Dermatophytosis
E. Melanoma in situ
2. A 65-year-old male farmer presents with an incidentally
found slightly discolored skin lesion on his forehead. He denies other symptoms.
He has a history of multiple squamous cell carcinomas and basal cell carcinomas
of skin, all treated with local resections. Physical examination reveals a 2.5
cm slightly erythematous area with a rough surface at his left forehead. No
other significant abnormalities are noted. An image of the biopsy is shown. What
disease is likely to develop from this lesion?
(Image: LWozniak&KWZielinski [CC BY-SA 3.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
B. Invasive melanoma
C. Merkel cell carcinoma
D. Sezary syndrome
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
3. Use this case
and this image for the next two questions. A 59-year-old man presents with
a slowly growing nodule at his left forearm. He has a history of diabetes. The
nodule has a smooth surface with dilated vessels. An image of the biopsy is
shown. What is the most important cause of this lesion?
(Image: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Abnormal keratinocyte turn over
B. Chronic irritation
C. Human papilloma virus
D. Insulin resistance
E. Sun exposure
4. A 59-year-old man presents with a slowly growing
nodule at his left forearm. The nodule has a smooth surface with dilated
vessels. An image of the biopsy is shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Actinic keratosis
B. Basal cell carcinoma
C. Cylindroma
D. Psoriasis
E. Tricholemmoma
5. Use this case
and this image for the next three questions. A 61-year-old woman presents
with a slowly growing painless skin nodule at her left upper lip. Her past
medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals a 3 mm papule
with scar appearing smooth surface. No other abnormality is noted. An image of the
biopsy is shown. What is likely to be found in this lesion?
(Image: LWozniak&KWZielinski [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Distant metastasis
B. Multifocality
C. Perineural invasion
D. Primitive hair follicles
E. Squamous pearls
6. A 61-year-old woman presents with a slowly growing
painless skin nodule at her left upper lip. Her past medical history is
unremarkable. Physical examination reveals a 3 mm papule with scar appearing
smooth surface. No other abnormality is noted. An image of the biopsy is shown.
What is the proper treatment?
(Image: LWozniak&KWZielinski [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Chemotherapy
B. Cryotherapy
C. Mohs surgery
D. Topical steroid
E. Wide excision
7. A 61-year-old woman presents with a slowly growing
painless skin nodule at her left upper lip. Her past medical history is
unremarkable. Physical examination reveals a 3 mm papule with scar appearing
smooth surface. No other abnormality is noted. An image of the biopsy is shown.
What is the diagnosis?
(Image: LWozniak&KWZielinski [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Actinic keratosis
B. Basal cell carcinoma
C. Cylindroma
D. Syringoma
E. Tricholemmoma
8. Use this case
and this image for the next two questions. A 55-year-old woman presents
with a waxy skin lesion at her left forearm. Physical examination reveals a 0.5
cm tan rough scaling macule. An image of the biopsy is shown. What is likely to
be found in this lesion?
(Image: LWozniak&KWZielinski [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Distant metastasis
B. Multifocality
C. Perineural invasion
D. Primitive hair follicles
E. Squamous pearls
9. A 55-year-old woman presents with a waxy skin
lesion at her left forearm. Physical examination reveals a 0.5 cm tan rough scaling
macule. An image of the biopsy is shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image: LWozniak&KWZielinski [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Actinic keratosis
B. Basal cell carcinoma
C. Cylindroma
D. Syringoma
E. Tricholemmoma
10. Use this image
this question. A 48-year-old man presents with a 0.8 cm painless nodule at his
forehead. Image of the biopsy is shown. Mutation of what gene is likely associated
with this lesion?
(Image: Ed Uthman, MD [CC BY-SA 2.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0)])
A. Beta-catenin
B. BRAF
C. CYLD
D. MSH2
E. PTCH
11. Use this case
and this image for the next two questions. A 51-year-old man presents with
a rapid growing painless nodule at his forehead. Image of the biopsy is shown. Per
immunohistochemistry studies, this lesion is positive for pan cytokeratin, CD56
and negative for CD45, and TTF 1. What additional marker is likely to be
positive?
(Image: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. CD3
B. CD20
C. CK7
D. CK20
E. Desmin
12. A 51-year-old man presents with a rapid growing painless
nodule at his forehead. Image of the biopsy is shown. Per immunohistochemistry
studies, this lesion is positive for pan cytokeratin, CD56 and negative for
CD45, and TTF 1. What is most likely the diagnosis?
(Image: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Basal cell carcinoma
B. Cylindroma
C. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
D. Merkel cell carcinoma
E. Poroma
13. Use this image
this question. A 71-year-old man presents with a pruritic skin lesion at
his right hands. The lesion is slightly raised with a scaly surface up to 1.5
cm in greatest dimension. He has a history of multiple squamous cell carcinoma
and melanoma for the last 10 years. An image of the biopsy is shown. These changes
are only seen in the epidermis. No atypical cells are noted in the dermis. Per
immunohistochemistry studies, no S-100 positive cells are seen beyond the basal
layer. What is the diagnosis?
(Image: KGH assumed (based on copyright claims). [CC
BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)])
A. Actinic keratosis
B. Basal cell carcinoma
C. Bowen disease
D. Invasive squamous cell carcinoma
E. Melanoma in situ
14. Use this case
and this image for the next two questions. A 57-year-old man presents with
a ulcerated mass on his left face. He has had multiple basal cell carcinoma and
melanoma. He has a 45 pack-year history of cigarette smoking and has been
working in a polyvinyl chloride manufacture
factory for 35 years. An image of the biopsy is shown. What is most likely causing
this lesions?
(Image: LWozniak&KWZielinski [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Cigarette smoking
B. Human papilloma virus
C. Molluscum contagiosum virus
D. Polyvinyl chloride
E. Sun exposure
15. A 57-year-old man presents with a ulcerated mass
on his left face. He has had multiple basal cell carcinoma and melanoma. He has
a 45 pack-year history of cigarette smoking and has been working in a polyvinyl
chloride manufacture factory for 35 years. An
image of the biopsy is shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image: LWozniak&KWZielinski [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Actinic keratosis
B. Bowen disease
C. Epidermal cyst
D. Squamous cell carcinoma
E. Tricholemmoma
16. Use this case
and this image for the next two questions. A 77-year-old man presents with
a pruritic rash on his back. He has had similar rash a year ago that regressed
without specific treatment. He has had multiple basal cell carcinomas and squamous
cell carcinomas. Physical examination reveals a 3.5 cm irregular erythematous
patch with fine scales at his left lower back. No other abnormality is noted. His
laboratory tests results are within normal range. An image of the biopsy is shown.
Initial immunohistochemistry studies reveal the cells with dark nuclei are
positive for CD3, but negative for CD20. What additional markers are needed to
confirm the diagnosis?
(Image: LWozniak&KWZielinski [CC BY-SA 3.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. CD4 and CD8
B. CD5 and CD23
C. CD15 and CD30
D. CK7 and CAM5.2
E. HMB45 and S100
17. A 77-year-old man presents with a pruritic rash on
his back. He has had similar rash a year ago that regressed without specific treatment.
He has had multiple basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas. Physical
examination reveals a 3.5 cm irregular erythematous patch with fine scales at
his left lower back. No other abnormality is noted. His laboratory tests
results are within normal range. An image of the biopsy is shown. Initial
immunohistochemistry studies reveal the cells with dark nuclei are positive for
CD3, but negative for CD20.
Additional studies reveal these cells are all positive
for CD4 and negative for CD8. What is the diagnosis?
(Image: LWozniak&KWZielinski [CC BY-SA 3.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Dermatophytosis
B. Lichen planus
C. Mycosis fungoides
D. Psoriasis
E. Sezary syndrome
18. Use this
image for this question. A 71-year-old male farmer presents with an
ulcerated mass at his chest. He does not have other symptoms. He has had multiple
squamous cell carcinomas and basal cell carcinomas of skin. Physical examination
reveals a 4.5 cm chest mass with ulceration. No lymphoadenopathy is noted.
Laboratory test is within normal range. An image of the biopsy is shown. Per
immunohistochemistry studies, these cells are predominantly CD4 positive and
CD8 negative. Scattered CD20 positive cells are seen in dermis. What is the diagnosis?
(Image: LWozniak&KWZielinski [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Bowen disease
B. Dermatophytosis
C. Lichen planus
D. Mycosis fungoides
E. Sezary syndrome
19. Use this case
and this image for the next two questions. A 77-year-old man presents with
fatigue and a 20 pound weight loss for the last two months. His past medical history
is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals diffuse erythematous changes of
his trunk and enlarged bilateral inguinal lymph nodes. Laboratory tests reveal
a hemoglobin of 7.5 g/dl (normal 12-18 g/dl). His white cell and platelet counts
are within normal range. An image of the peripheral blood smear is shown. Similar
cells are seen in his lymph node biopsy. What marker is likely to be positive
for these nucleated cells shown?
(Image: El*Falaf [CC BY-SA 3.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. CD3
B. CD11c
C. CD20
D. CD30
E. CD138
20. A 77-year-old man presents with fatigue and a 20
pound weight loss for the last two months. His past medical history is
unremarkable. Physical examination reveals diffuse erythematous changes of his
trunk and enlarged bilateral inguinal lymph nodes. Laboratory tests reveal a
hemoglobin of 7.5 g/dl (normal 12-18 g/dl). His white cell and platelet counts
are within normal range. An image of the peripheral blood smear is shown. Similar
cells are seen in his lymph node biopsy. What is most likely the diagnosis?
(Image: El*Falaf [CC BY-SA 3.0
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
A. Adult T cell leukemia
B. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
C. Chronic myeloid leukemia
D. Hairy cell leukemia
E. Sezary syndrome
Back to skin
tumors
Back to contents










Comments
Post a Comment