Practice questions myeloid neoplasms 2
Practice
questions

Answers
Back to myeloid neoplasm
Back to contents
Myeloid
neoplasms II
©
Jun Wang, MD, PhD
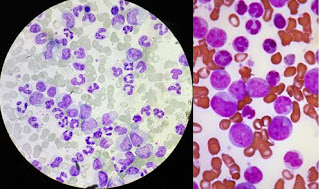
1. Use this case and image for the next five questions. A 22-year-old woman
presents with large bruises on her skin and gum bleeding for 5 days. Her past
medical history is unremarkable. She does not smoke nor drink alcohol. Physical
examination reveal purpuric spots at her upper chest and arms. A few small
ulcers are seen in her gum. No lymphadenopathy is seen. Laboratory tests reveal
a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal 12-16 g/dl), white cell count of 3.5 x 109/L (normal 5-11
x 109/L), platelet count 75 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x 109/L).
PT and
aPTT are within normal range. An image of the peripheral blood smear is shown.
What test would confirm the diagnosis?
(Image credit: The Armed
Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) [Public domain])
A. Biopsy of the gum ulcer
B. Blood culture
C. Flow cytometry
D. Immunofixation
E. Monospot
2. A 22-year-old woman
presents with large bruises on her skin and gum bleeding for 5 days. Her past
medical history is unremarkable. She does not smoke nor drink alcohol. Physical
examination reveal purpuric spots at her upper chest and arms. A few small
ulcers are seen in her gum. No lymphadenopathy is seen. Laboratory tests reveal
a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal 12-16 g/dl), white cell count of 3.5 x 109/L (normal 5-11
x 109/L), platelet count 75 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x 109/L).
PT and
aPTT are within normal range. An image of the peripheral blood smear is shown.
What is most likely the cause of her low platelet count?
(Image credit: The Armed
Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) [Public domain])
A. ADAMTS13 mutation
B. Autoimmune process
C. Endothelial injury
D. Marrow suppression
E. Viral infection
3. A 22-year-old woman
presents with large bruises on her skin and gum bleeding for 5 days. Her past
medical history is unremarkable. She does not smoke nor drink alcohol. Physical
examination reveal purpuric spots at her upper chest and arms. A few small ulcers
are seen in her gum. No lymphadenopathy is seen. Laboratory tests reveal a
hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal 12-16 g/dl), white cell count of 3.5 x 109/L (normal 5-11
x 109/L), platelet count 75 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x 109/L).
PT and
aPTT are within normal range. An image of the peripheral blood smear is shown.
Flow cytometry studies
reveal abnormal white cells expressing CD33 and CD34, but not TdT. These cells
occupy approximately 17% of white cells. What test results would confirm the diagnosis?
(Image credit: The Armed
Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) [Public domain])
A. Biopsy of the gum ulcer
B. Blood culture
C. Cytogenetic studies
D. Immunofixation
E. Monospot
4. A 22-year-old woman
presents with large bruises on her skin and gum bleeding for 5 days. Her past
medical history is unremarkable. She does not smoke nor drink alcohol. Physical
examination reveal purpuric spots at her upper chest and arms. A few small
ulcers are seen in her gum. No lymphadenopathy is seen. Laboratory tests reveal
a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal 12-16 g/dl), white cell count of 3.5 x 109/L (normal 5-11
x 109/L), platelet count 75 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x 109/L).
PT and
aPTT are within normal range. An image of the peripheral blood smear is shown.
Flow cytometry studies reveal
abnormal white cells expressing CD33 and CD34, but not TdT. These cells occupy
approximately 17% of white cells. FISH studies reveals t(8;21)(q22;q22). What
is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: The Armed
Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) [Public domain])
A. Acute myeloid leukemia
B. Acute promyelocytic
leukemia
C. Acute lymphoblastic
leukemia
D. Acute myelomonocytic
leukemia
E. Chronic myelogenous
leukemia
5. A 22-year-old woman
presents with large bruises on her skin and gum bleeding for 5 days. Her past
medical history is unremarkable. She does not smoke nor drink alcohol. Physical
examination reveal purpuric spots at her upper chest and arms. A few small
ulcers are seen in her gum. No lymphadenopathy is seen. Laboratory tests reveal
a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal 12-16 g/dl), white cell count of 3.5 x 109/L (normal 5-11
x 109/L), and platelet count 75 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x
109/L). PT
and aPTT are within normal range. An image of the peripheral blood smear is
shown.
Flow cytometry studies reveal
abnormal white cells expressing CD33 and CD34, but not TdT. These cells occupy
approximately 17% of white cells. FISH studies reveals t(8;21)(q22;q22).
Abnormality of what gene is associated with these findings?
(Image credit: The Armed
Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) [Public domain])
A. ABL
B. CBF-beta
C. JAK2
D. RAR alpha
E. RUNX1
6. Use this case and image for the next five questions. A 28-year-old
man presents with fatigue and low-grade fever for a week. He develops mild
gingival bleeding in the last 2 day. His past medical history is unremarkable.
Physical examination reveals no significant abnormalities except pale skin, ecchymosis
and pinpoint bleeding of his gingiva and oral mucosa. Laboratory tests reveals
a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal 14-18 g/dl), white cell of 3.7 x 109/L
(normal 5-11
x 109/L), and platelet count 62 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x
109/L).
WBC differential reveals 20% lymphocytes, 16% monocytes, 5% eosinophils, 1% basophils,
52% atypical cells. An image of the peripheral blood smear is shown. What is
most likely the diagnosis?
(Image credit: The Armed
Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) [Public domain])
A. Acute myeloid leukemia with
inv(16)(p13.1;q22)
B. Acute promyelocytic
leukemia
C. Acute lymphoblastic
leukemia
D. Chronic myelogenous
leukemia
E. Leukemoid reaction
7. A 28-year-old man
presents with fatigue and low-grade fever for a week. He develops mild gingival
bleeding in the last 2 day. His past medical history is unremarkable. Physical
examination reveals no significant abnormalities except pale skin, ecchymosis
and pin point bleeding of his gingiva and oral mucosa. Laboratory tests reveals
a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal 14-18 g/dl), white cell of 3.7 x 109/L
(normal 5-11
x 109/L), and platelet count 62 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x
109/L).
WBC differential reveals 20% lymphocytes, 16% monocytes, 5% eosinophils, 1%
basophils, 52% atypical cells. An image of the peripheral blood smear is shown.
Abnormality of what gene is most likely associated with these findings?

(Image credit: The Armed
Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) [Public domain])
A. ABL
B. CBF-beta
C. JAK2
D. RAR alpha
E. RUNX1
8. A 28-year-old man
presents with fatigue and low-grade fever for a week. He develops mild gingival
bleeding in the last 2 day. His past medical history is unremarkable. Physical
examination reveals no significant abnormalities except pale skin, ecchymosis
and pin point bleeding of his gingiva and oral mucosa. Laboratory tests reveals
a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal 14-18 g/dl), white cell of 3.7 x 109/L
(normal 5-11
x 109/L), and platelet count 62 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x
109/L).
WBC differential reveals 20% lymphocytes, 16% monocytes, 5% eosinophils, 1%
basophils, 52% atypical cells. An image of the peripheral blood smear is shown.
What cytogenetics abnormality is likely associated with these findings?
(Image credit: The Armed
Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) [Public domain])
A. t(8;21)(q22;q22)
B. inv(16)(p13.1;q22)
C. t(15;17)(q22;q12)
D. t(9;22) (q34;q11)
E. 7q-
9. A 28-year-old man
presents with fatigue and low-grade fever for a week. He develops mild gingival
bleeding in the last 2 day. His past medical history is unremarkable. Physical
examination reveals no significant abnormalities except pale skin, ecchymosis
and pin point bleeding of his gingiva and oral mucosa. Laboratory tests reveals
a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal 14-18 g/dl), white cell of 3.7 x 109/L
(normal 5-11
x 109/L), and platelet count 62 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x
109/L).
WBC differential reveals 20% lymphocytes, 16% monocytes, 5% eosinophils, 1%
basophils, and 52% atypical cells. An image of the peripheral blood smear is
shown. What medication should be included in his treatment?
(Image credit: The Armed
Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) [Public domain])
A. All-trans retinoid acid
B. Folate
C. Iron supplementation
D. Vitamin B12
E. Vitamin K
10. A 28-year-old man
presents with fatigue and low-grade fever for a week. He develops mild gingival
bleeding in the last 2 day. His past medical history is unremarkable. Physical
examination reveals no significant abnormalities except pale skin, ecchymosis
and pin point bleeding of his gingiva and oral mucosa. Laboratory tests reveals
a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (normal 14-18 g/dl), white cell of 3.7 x 109/L
(normal 5-11
x 109/L), and platelet count 62 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x
109/L).
WBC differential reveals 20% lymphocytes, 16% monocytes, 5% eosinophils, 1%
basophils, 52% atypical cells. An image of the peripheral blood smear is shown.
He was admitted and
chemotherapy was started. The second day of treatment, he develops dizziness
and severe gingival bleeding. Laboratory tests reveals a hemoglobin of 6.3 g/dl
(normal 14-18 g/dl), white cell of 1.5 x 109/L (normal 5-11 x 109/L),
and platelet count 45 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x 109/L). He has an aPTT of 66 s
(normal 22.7-34.1 s), PT of 32 s (normal 11.7-14.6s), fibrinogen of 77 mg/dl
(normal 225-480 mg/dl) and D-dimer of 2500 FEU ng/ml (normal 0-500 FEU ng/ml). Blood
culture is negative. What is causing his presentations?
(Image credit: The Armed
Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) [Public domain])
A. Disseminated
intravascular coagulation
B. Heparin induced
thrombocytopenia
C. Immune thrombocytopenic
purpura
D. Sepsis
E. Vitamin K deficiency
11. Use this image for the next question. A 41-year-old woman
presents with acute abdominal pain for 5 hours. She does not have fever or
other symptoms. Her past medical history is unremarkable. She does not smoke
cigarette nor drink alcohol. Physical examination reveals no significant
findings. Laboratory tests reveals a hemoglobin of 11.5 g/dl (normal 12-16
g/dl), white cell of 18.5 x 109/L (normal 5-11 x 109/L), and
platelet count 125 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x 109/L). An
image of her peripheral blood smear is shown. Approximately 35% of white cells are
those shown in the image. Per flow cytometry, these cells express CD33 and CD34
but not CD2, CD3, TdT or immunoglobulin. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: The Armed
Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) [Public domain])
A. Acute myeloid leukemia
B. Acute promyelocytic
leukemia
C. Acute lymphoblastic
leukemia
D. Chronic myelogenous
leukemia
E. Leukemoid reaction
12. Use this case and image for the next five questions. A 61-year-old
man presents with fatigue and progressive abdominal distention for 3 months. He
has a history of low-grade prostate cancer 10 years ago that was treated with
radical prostatectomy. He does not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol. Physical
examination reveals pallor skin, 1+ pedal edema and bulging abdomen. His spleen
is non tender and extend to 4 cm below left costal margin. No dilated veins are
seen. No other abnormality is noted. Laboratory tests reveals a hemoglobin of
9.2 g/dl (normal 14-18 g/dl), white cell of 42 x 109/L (normal 5-11 x 109/L),
and platelet count 784 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x 109/L).
White differential reveals 65% mature neutrophils, 5% band neutrophils, 3%
myeloblasts, 10% lymphocytes, 2% eosinophils, 9% monocytes and 4% basophils. An
image of her peripheral blood smear is shown. Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase
(LAP) score is 11 (normal 20-100). Other test results including prostate
specific antigen are within normal range. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: J3D3 [CC
BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)])
A. Acute myeloid leukemia
B. Chronic myelogenous
leukemia
C. Chronic myelomonocytic
leukemia
D. Essential
thromobocytosis
E. Leukemoid reaction
13. A 61-year-old man
presents with fatigue and progressive abdominal distention for 3 months. He has
a history of low-grade prostate cancer 10 years ago that was treated with
radical prostatectomy. He does not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol. Physical
examination reveals pallor skin, 1+ pedal edema and bulging abdomen. His spleen
is non tender and extend to 4 cm below left costal margin. No dilated veins are
seen. No other abnormality is noted. Laboratory tests reveals a hemoglobin of
9.2 g/dl (normal 14-18 g/dl), white cell of 42 x 109/L (normal 5-11 x 109/L),
and platelet count 784 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x 109/L).
White differential reveals 65% mature neutrophils, 5% band neutrophils, 3%
myeloblasts, 10% lymphocytes, 2% eosinophils, 9% monocytes and 4% basophils. An
image of her peripheral blood smear is shown. Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase
(LAP) score is 11 (normal 20-100). Other test results including prostate
specific antigen are within normal range. What chromosome abnormality is likely
associated with these findings?
(Image credit: J3D3 [CC
BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)])
A. inv(16)(p13.1;q22)
B. t(8;21)(q22;q22)
C. t(9;22) (q34;q11)
D. t(11;14)(q13;q32)
E. t(15;17)(q22;q12)
14. A 61-year-old man
presents with fatigue and progressive abdominal distention for 3 months. He has
a history of low-grade prostate cancer 10 years ago that was treated with
radical prostatectomy. He does not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol. Physical
examination reveals pallor skin, 1+ pedal edema and bulging abdomen. His spleen
is non tender and extend to 4 cm below left costal margin. No dilated veins are
seen. No other abnormality is noted. Laboratory tests reveals a hemoglobin of
9.2 g/dl (normal 14-18 g/dl), white cell of 42 x 109/L (normal 5-11 x 109/L),
and platelet count 784 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x 109/L).
White differential reveals 65% mature neutrophils, 5% band neutrophils, 3%
myeloblasts, 10% lymphocytes, 2% eosinophils, 9% monocytes and 4% basophils. An
image of her peripheral blood smear is shown. Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase
(LAP) score is 11 (normal 20-100). Other test results including prostate
specific antigen are within normal range. Abnormality of what gene is likely
associated with these findings?
(Image credit: J3D3 [CC
BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)])
A. BCR
B. CBF-beta
C. JAK2
D. RAR alpha
E. RUNX1T1
15. A 61-year-old man
presents with fatigue and progressive abdominal distention for 3 months. He has
a history of low-grade prostate cancer 10 years ago that was treated with
radical prostatectomy. He does not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol. Physical
examination reveals pallor skin, 1+ pedal edema and bulging abdomen. His spleen
is non tender and extend to 4 cm below left costal margin. No dilated veins are
seen. No other abnormality is noted. Laboratory tests reveals a hemoglobin of
9.2 g/dl (normal 14-18 g/dl), white cell of 42 x 109/L (normal 5-11 x 109/L),
and platelet count 784 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x 109/L).
White differential reveals 65% mature neutrophils, 5% band neutrophils, 3%
myeloblasts, 10% lymphocytes, 2% eosinophils, 9% monocytes and 4% basophils. An
image of her peripheral blood smear is shown. Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase
(LAP) score is 11 (normal 20-100). Other test results including prostate
specific antigen are within normal range. What is most likely the cause of his
spleen findings?
(Image credit: J3D3 [CC
BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)])
A. Bacterial infection
B. Extramedullary
hematopoiesis
C. Metastatic prostate
cancer
D. Portal hypertension
E. Splenic vein thrombosis
16. A 61-year-old man
presents with fatigue and progressive abdominal distention for 3 months. He has
a history of low-grade prostate cancer 10 years ago that was treated with
radical prostatectomy. He does not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol. Physical
examination reveals pallor skin, 1+ pedal edema and bulging abdomen. His spleen
is non tender and extend to 4 cm below left costal margin. No dilated veins are
seen. No other abnormality is noted. Laboratory tests reveals a hemoglobin of
9.2 g/dl (normal 14-18 g/dl), white cell of 42 x 109/L (normal 5-11 x 109/L),
and platelet count 784 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x 109/L).
White differential reveals 65% mature neutrophils, 5% band neutrophils, 3%
myeloblasts, 10% lymphocytes, 2% eosinophils, 9% monocytes and 4% basophils. An
image of her peripheral blood smear is shown. Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase
(LAP) score is 11 (normal 20-100). Other test results including prostate
specific antigen are within normal range.
He was treated with Imatinib. 3
years later he develops acute abdominal pain. Laboratory tests reveals a
hemoglobin of 7.5 g/dl (normal
14-18 g/dl), white cell of 67 x 109/L (normal 5-11 x 109/L), and
platelet count 78 x 109/L (normal 150-450 x 109/L). 45% of
the white cells are those shown in the additional image of his peripheral blood
smear. These cells express CD34, but not TdT. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: J3D3 [CC
BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)], and Public Health Image
Library)
A. Acute myeloid leukemia
B. Acute lymphoblast
leukemia
C. Chronic myeloid
leukemia, accelerated phase
D. Chronic myeloid
leukemia, blast phase
E. Primary myelofibrosis
Back to myeloid neoplasm
Back to contents



Comments
Post a Comment