Practice questions Ib, female genital tract
Practice questions Ib, female genital tract
Pathology of vulva, vagina and cervix
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
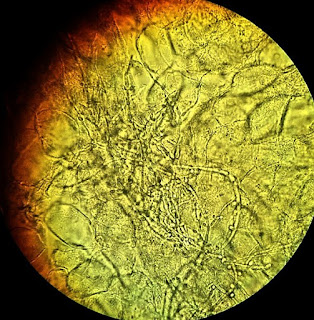
1. Use this image for the next question. A 42-year-old
woman presents with pruritus and burning sensation at vulvar, with progressively
increasing thick white vaginal discharge for 3 months. She denies dysuria or
dyspareunia. She has type II diabetes for 5 years. Physical examination reveals
irregular erythematous changes of vulva and vaginal mucosa. An image of the wet
mount preparation is shown. What is most likely causing these changes?
(Image credit: Mikael Häggström, used with permission. / CC0)
A. Candida
B. Chlamydia trachomatis
C. Gonorrhea
D. Herpes simplex
E. Human papillomavirus
2. Use this case for the next two questions. A 29-year-old
woman presents with intermittent pruritis and burning sensation of her vulva
for 4 months. She has had yellow green malodorous vaginal discharge. She does
not have other symptoms. Her was found to be HIV positive 6 months ago. She is
sexually active with multiple partners. She has a 10 pack-year history of
cigarette smoking but does not drink alcohol. General physical examination is unremarkable.
No lymphadenopathy is noted. Pelvic exam reveals mild cervical tenderness. The cervix
is pink with focal punctate erythematous changes. There is thin green frothy malodorous
discharge. What test is likely to reveal cause of her presentations?
A. Anti-cardiolipin antibody levels
B. Cervical biopsy
C. Gram stain of discharge
D. Wet mount preparation
E. Whiff test
3. Use this image for the next question. A 29-year-old
woman presents with intermittent pruritis and burning sensation of her vulva
for 4 months. She has had yellow green malodorous vaginal discharge. She does
not have other symptoms. Her was found to be HIV positive 6 months ago. She is
sexually active with multiple partners. She has a 10 pack-year history of
cigarette smoking but does not drink alcohol. General physical examination is unremarkable.
No lymphadenopathy is noted. Pelvic exam reveals mild cervical tenderness. The cervix
is pink with focal punctate erythematous changes. There is thin green frothy malodorous
discharge. An image of her discharge with Giemsa stain is shown. What is the diagnosis?
A. Bacterial vaginosis
B. Candida
C. Chlamydia
D. Herpes
E. Trichomoniasis
4. Use this case and image for the next two questions. A
22-year-old asymptomatic G1P0 woman presents for initial prenatal care. Her
past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals thin vaginal
discharge with a fishy odor. No other abnormality is noted. An image of her
vaginal discharge wet mount is shown. What additional finding is likely seen?
(Image credit: CDC/ M. Rein / Public domain)
A. Elevated vaginal pH
B. Fungal pseudohyphae
C. Gram negative diplococci
D. Motile protozoa
E. Squamous cells with large hyperchromatic irregular nuclei
5. A
22-year-old asymptomatic G1P0 woman presents for initial prenatal care. Her
past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals thin vaginal
discharge with a fishy odor. No other abnormality is noted. An image of her
vaginal discharge wet mount is shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: CDC/ M. Rein / Public domain)
A. Bacterial vaginosis
B. Candida
C. Chlamydia
D. Herpes
E. Trichomoniasis
6. Use this image for the next question. A 25-year-old
asymptomatic G2P1 woman presents for prenatal care. She has a history of
asthma, type 1 diabetes, and vaginal trichomoniasis. Physical examination reveals
no significant abnormalities. Cervical exam reveals watery discharge, with
focal cervical ulceration. An image of her Pap test is shown. What is the
diagnosis?
(Image credit: Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA / CC BY
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0))
A. Bacterial vaginosis
B. Candida
C. Chlamydia
D. Herpes
E. Trichomonas vaginalis
7. Use this case and image for the next two questions. A
31-year-old woman presents for intermittent vaginal bleeding. She does not have
other symptoms. She has a history of recurrent trichomoniasis. She is sexually
active with multiple partners. Physical examination reveals no significant
abnormality. No lymphadepathy is noted. Cervical exam reveals a 1.5 cm mass with
cauliflower like surface. Focally there are hemorrhagic changes. An image of her
Pap test is shown. Normal glandular components are present. No other abnormality
is noted. What is most likely associated with her presentations?
(Image credit: Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA / CC BY
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0))
A. Candida albicans
B. Chlamydia trachomatis
C. Herpes simplex
D. Human papillomavirus
E. Trichomonas vaginalis
8. A 31-year-old
woman presents for intermittent vaginal bleeding. She does not have other
symptoms. She has a history of recurrent trichomoniasis. She is sexually active
with multiple partners. Physical examination reveals no significant
abnormality. No lymphadepathy is noted. Cervical exam reveals a 0.5 cm mass with
cauliflower like surface. Focally there are hemorrhagic changes. An image of her
Pap test is shown. Normal glandular components are present. No other abnormality
is noted. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA / CC BY (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0))
A. Chlamydial vaginitis
B. Condyloma acuminatum
C. Endocervical adenocarcinoma
D. Gonorrhea
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
9. Use this case and image for the next two questions. A
61-year-old woman presents with progressively increased vaginal discharge for 4
months, after she resumed sexual activity for 6 months. Prior to this, she had
been sexually abstinent for 7 years. Her LMP was at age 49. She denies other
symptoms. Her past medical history including candida vaginitis 15 years ago,
and type 2 diabetes since age 35. She does not smoke cigarette nor drink
alcohol. Physical examination and routine laboratory tests are unremarkable.
Initial Pap smear reveals atypical squamous cells. Colposcopy exam reveals a
1.5 cm polypoid growth at the external os. The growth is removed and an image
of the microscopic exam is shown. What is most likely associated with her
presentations?
(Image credit: Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA / CC BY (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0))
A. Candida albicans
B. Chlamydia trachomatis
C. Estrogen insufficiency
D. Human papillomavirus
E. Hyperglycemia
10. A 61-year-old
woman presents with progressively increased vaginal discharge for 4 months, after
she resumed sexual activity for 6 months. Prior to this, she had been sexually abstinent
for 7 years. Her LMP was at age 49. She denies other symptoms. Her past medical
history including candida vaginitis 15 years ago, and type 2 diabetes since age
35. She does not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol. Physical examination and
routine laboratory tests are unremarkable. Initial Pap smear reveals atypical
squamous cells. Colposcopy exam reveals a 1.5 cm polypoid growth at the external
os. The growth is removed and an image of the microscopic exam is shown. What
is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA / CC BY (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0))
A. Candidal vaginitis
B. Condyloma acuminatum
C. Endocervical adenocarcinoma
D. Severe squamous dysplasia (CIN III)
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
11. Use this case and image for the next three questions.
A 32-year-old asymptomatic woman presents for atypical squamous cells on
routine Pap test. Her past medical history including trichomoniasis and multiple
times of atypical squamous cells identified on Pap tests. She was found to be
HIV positive 6 months ago. She is sexually active with a few men. She smokes a
pack of cigarette for 5 years, and drinks alcohol occasionally. She has been
using intravenous heroine for 2 years. Physical examination did not reveal
significant abnormality. Her laboratory tests including CBC are within normal range.
Colposcopy exam are unremarkable and random biopsies were performed. An image
of the microscopic exam is shown. What is most likely associated with her
presentations?
(Image credit: Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA / CC BY
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0))
A. Candida albicans
B. Human herpes virus simplex
C. Human immunodeficiency virus
D. Human papillomavirus
E. Trichomonas vaginalis
12. A
32-year-old asymptomatic woman presents for atypical squamous cells on routine Pap
test. Her past medical history including trichomoniasis and multiple times of
atypical squamous cells identified on Pap tests. She was found to be HIV
positive 6 months ago. She is sexually active with a few men. She smokes a pack
of cigarette for 5 years, and drinks alcohol occasionally. She has been using
intravenous heroine for 2 years. Physical examination did not reveal significant
abnormality. Her laboratory tests including CBC are within normal range. Colposcopy
exam are unremarkable and random biopsies were performed. An image of the
microscopic exam is shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA / CC BY
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0))
A. Condyloma
B. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade III
C. Endocervical adenocarcinoma
D. Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
13. A 32-year-old
asymptomatic woman presents for atypical squamous cells on routine Pap test.
Her past medical history including trichomoniasis and multiple times of
atypical squamous cells identified on Pap tests. She was found to be HIV
positive 6 months ago. She is sexually active with a few men. She smokes a pack
of cigarette for 5 years, and drinks alcohol occasionally. She has been using
intravenous heroine for 2 years. Physical examination did not reveal significant
abnormality. Her laboratory tests including CBC are within normal range. Colposcopy
exam are unremarkable and random biopsies were performed. An image of the
microscopic exam is shown. What is most likely to develop if she is not treated
properly?
(Image credit: Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA / CC BY
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0))
A. Chronic pelvic disease
B. Ectopic pregnancy
C. Endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma
D. Regression
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
14. Use this case and image for the next two questions. A
19-year-old woman presents with multiple pruritic skin lesions at her lower
abdomen. She denies other symptoms. Physical examination is unremarkable. Images
of the skin lesion and microscopic exam are shown. What is the cause of these lesions?
(Image credit: Evanherk / CC BY-SA (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/);
Ed Uthman, MD. / CC BY (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0))
A. Human herpes virus simplex
B. Human papillomavirus
C. Klebsiella granulomatis
D. Molluscum contagiosum virus
E. Treponema pallidum
15. A 19-year-old
woman presents with multiple pruritic skin lesions at her lower abdomen. She
denies other symptoms. Physical examination is unremarkable. Images of the skin
lesion and microscopic exam are shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Evanherk / CC BY-SA (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/);
Ed Uthman, MD. / CC BY (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0))
A. Chancroid
B. Herpes
C. Molluscum contagiosum
D. Secondary syphilis
E. Wart
16. Use this case and image for the next two questions. A
66-year-old woman presents with itchy and burning sensation of her genital area.
She denies other symptoms. Her past medical history is unremarkable. She does
not smoke cigarette, but drinks wines occasionally. She is sexually inactive.
Physical examination reveals thinned skin in her vulva. No other abnormalities
are noted. An image of the microscopic exam of her biopsy is shown. Special
stains do not reveal fungal elements. If not treated, the patient has an
increased risk for what disease?
(Image credit: Nephron / CC BY-SA
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0))
A. Chronic pelvic disease
B. Endocervical adenocarcinoma
C. Recurrent fungal infection
D. Sepsis
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
17. A 66-year-old
woman presents with itchy and burning sensation of her genital area. She denies
other symptoms. Her past medical history is unremarkable. She does not smoke
cigarette, but drinks wines occasionally. She is sexually inactive. Physical examination
reveals thinned skin in her vulva. No other abnormalities are noted. An image
of the microscopic exam of her biopsy is shown. Special stains do not reveal
fungal elements. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Nephron / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0))
A. Condyloma
B. Dermatophytosis
C. Lichen sclerosis et atrophicus
D. Paget disease
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
18. Use this case and image for the next two questions. A
24-year-old woman presents with itchy and burning sensation of her genital area.
She denies other symptoms. She has a history recurrent urinary tract infection,
and she never had a pap test prior. Physical examination reveals focal erythematous
changes of her vulva and vaginal wall. No significant discharge is noted. Pap
test reveals fungal pseudo hyphae and scattered atypical glandular cells. An
image of her cervical biopsy is shown. What is most likely associated with the
findings seen in her cervical biopsy?
(Image credit: Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA / CC BY
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0))
A. Actinomycete
B. Candida albican
C. Gardnerella vaginalis
D. Human papillomavirus
E. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
19. A 24-year-old
woman presents with itchy and burning sensation of her genital area. She denies
other symptoms. She has a history recurrent urinary tract infection, and she never
had a pap test prior. Physical examination reveals focal erythematous changes
of her vulva and vaginal wall. No significant discharge is noted. Pap test
reveals fungal pseudo hyphae and scattered atypical glandular cells. An image
of her cervical biopsy is shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA / CC BY
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0))
A. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) grade III
B. Chronic cervicitis
C. Endocervical adenocarcinoma
D. Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
20. Use this case and image for the next two questions. A
35-year-old woman presents with postcoital bleeding for 4 months. She denies
other symptoms. Her past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination
is unremarkable. Gynecological examination reveals a 1.4 cm irregular growth at
her cervix. Radiologic examinations reveal a mass confined to cervix. No additional
abnormalities are noted. An image of her biopsy is shown. What is most likely
associated with the findings seen in her cervical biopsy?
(Image credit: cnicholsonpath)
A. Chronic inflammation
B. Estrogen effect
C. Human herpes virus
D. Human papillomavirus
E. p53 mutation
21. Use this case and image for the next two questions. A
35-year-old woman presents with postcoital bleeding for 4 months. She denies
other symptoms. Her past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination
is unremarkable. Gynecological examination reveals a 1.4 cm irregular growth at
her cervix. Radiologic examinations reveal a mass confined to cervix. No additional
abnormalities are noted. An image of her biopsy is shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: cnicholsonpath)
A. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) grade III
B. Endocervical adenocarcinoma
C. Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ
D. Endometrial adenocarcinoma, endometrioid type
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
22. Use this case and image for the next two questions. A
49-year-old woman presents with irregular vaginal bleeding and a foul discharge
for 3 months. Her past medical history is unremarkable. Gynecological exam
reveals a 2.3 cm mass at her cervix. Microscopic
examination of her biopsy is similar to the image shown. What is
most likely associated with the findings seen in her cervical biopsy?
(Image credit: Yale Rosen / CC BY-SA
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0))
A. Chlamydia trachomatis
B. Estrogen effect
C. Human herpes virus
D. Human papillomavirus
E. p53 mutation
23. A 49-year-old
woman presents with irregular vaginal bleeding and a foul discharge for 3
months. Her past medical history is unremarkable. Gynecological exam reveals a
2.3 cm mass at her cervix. Microscopic
examination of her biopsy is similar to the image shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Yale Rosen / CC BY-SA
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0))
A. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) grade III
B. Endocervical adenocarcinoma
C. Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ
D. Endometrial adenocarcinoma, endometrioid type
E. Squamous cell carcinoma











Comments
Post a Comment