Sepsis
Sepsis
Updated: 06/28/2022
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
Definition
- Life threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection
General features
- Organ dysfunction identified by acute change of 2 or more points in total SOFA score or qSOFA
- Likely prolonged ICU stay
- Relatively high mortality rate
- Commonly associated with infections of injury or internal organs and perforation/rupture of abdominal/pelvic structures
- Most commonly caused by bacterial infections, but can be caused by virus or fungi
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS)
- A term being abandoned since 2016
- Still being used clinically
- Poor mortality prediction comparing with Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA)
- Clinical responses to either infectious or non-infectious causes
Sequential Organ failure Assessment (SOFA)
- A systemic evaluation of organ function
- Performed in critically ill patients with suspected sepsis
- Systems involved
o Cardiovascular: Blood pressure
o Neurological: Coma scale
o Respiratory: PaO2/FIO2
o Coagulation: Platelets count
o Liver function: Bilirubin
o Renal function: Urine output, Creatinine
- An increase of score of 2 or more from baseline associated with significantly increased risk of mortality
- Baseline SOFA score is presumed to be zero unless pt has known organ dysfunction prior to infection
Quick SOFA (qSOFA)
- Simplified criteria to identify high risk patients with suspected infection
- Similar predictive validity
- An increase of score of 2 or more from baseline associated with significantly increased risk of mortality
- Baseline SOFA score is presumed to be zero unless pt has known organ dysfunction prior to infection
- Three criteria
o Respiratory rate 22/min or greater
o Altered mentation
o Systolic blood pressure 100 mm Hg or lower
Risk factors
- Intensive care unit admission
- Bacteremia
- ≥65 years
- Immunocompromised: Deficiency or suppression
- Diabetes and obesity
- Underlying malignancy
- Community acquired pneumonia
- Previous hospitalization
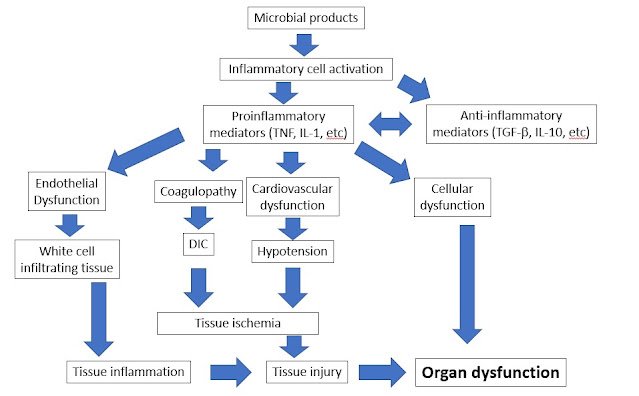
Key pathogenesis
- Excessive inflammatory reaction to infection
- Over activation of proinflammatory cytokines, growth factors, etc, such as TNF and IL-1
- Continuous activation of inflammatory cells and release of more cytokines
- Systemic dysfunction
o Endothelial dysfunction: elevated adhesin promotes leukocytes infiltrate surrounding tissue
o Coagulopathy: Activation of coagulation cascades may lead to disseminated intravascular coagulation
o Cellular dysfunction: Increased catabolism, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, etc
o Cardiovascular dysfunction: Decreased vascular resistance, normal or increased cardiac output, reduced ejection fraction
- Tissue hypoperfusion leads to septic shock
Pathophysiology
Clinical presentations
- Symptoms and signs associated with site of infection
- Arterial hypotension
- Fever
- Tachypnea
- Tachycardia
- Warm and flushed skin in early phase
- Cool skin if septic shock occurs
- Altered mental status
- Oliguria or anuria
- Ileus or absent bowel sound
Key Laboratory findings
- Reactive leukocytosis
- Thrombocytopenia
- Coagulopathy
- Hyperglycemia
- Elevated plasma C-reactive protein
- Arterial hypoxia
- Hyperlactatemia
- Results of organ dysfunction
o Kidney: Elevated creatinine
o Liver: Hyperbilirubinemia
o Adrenal: Hyponatremia, hyperkalemia
- Microbiology studies: Positive culture NOT necessary, many pts have negative culture and empiric antibiotics can be issue without culture results
Diagnosis
- Based on clinical and laboratory findings
- Organ dysfunction identified by acute change of 2 or more points in total SOFA score or qSOFA
- Symptoms and signs of infection
- Positive culture results, or clinical response to antibiotic treatments
Management
- Supportive management of organ dysfunction
o Vasopressor
o Activated protein C
o Corticosteroid
o Glycemic control
o Resuscitation from septic shock
- Identification and treatment of underlying infection
o Empiric antibiotics
Back to septic shock
Back to shock
Back to contents
Comments
Post a Comment