Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease
Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease
Updated: 09/14/2022
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
General features
- Post-capillary pulmonary hypertension
- Commonly seen in pts with heart failure
- Usually poor prognosis
Subclassification
- Isolated post-capillary PH (Ipc-PH): Elevated mPAP solely due to passive transmission of increased left-sided filling pressure to the pulmonary circulation
- Combined post- and precapillary PH (Cpc-PH): Elevated mPAP due to passive transmission of increased left-sided filling pressures with superimposed pulmonary vascular disease
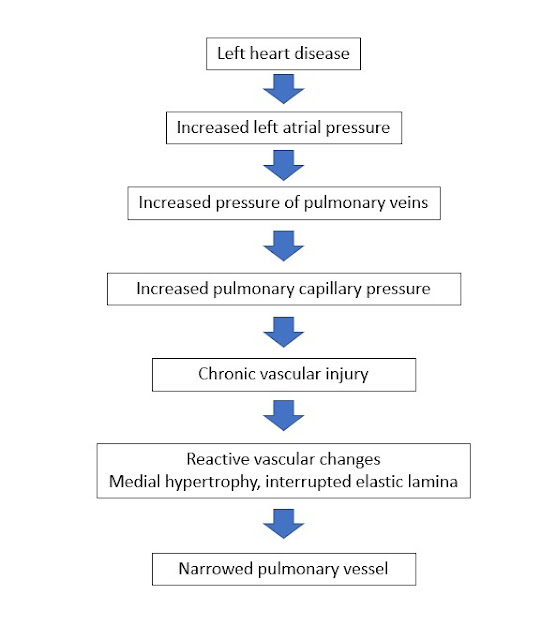
Pathogenesis
- Response to increase in left-side filling pressure
Clinical features
- Presentation of left heart diseases
- History of left heart diseases: infarct, etc
- Left ventricular dysfunction
- Pulmonary crackles
- S3 or S4 heart sound
- Presentation of right heart failure
- Loud P2
- Right ventricular heave
- Elevated jugular vein
- Hepatomegaly
- Presentation of pulmonary hypertension
Key morphological features
- Proliferative vasculopathy
Diagnosis
- Confirmation of pulmonary hypertension
- Right heart catheterization
- PAPm ≥ 25 mm Hg
- PAWP > 15 mm Hg
- Pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) ≥ 3 mm Hg if Cpc-PH
- PVR < 3 mm Hg if Ipc-PH
Treatment
- Management of underlying left heart diseases
- Systemic vasodilator
Back to pulmonary hypertension
Back to contents
Comments
Post a Comment