Pulmonary hypertension due to pulmonary artery obstruction
Pulmonary hypertension due to pulmonary artery obstruction
Updated: 08/25/2022
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
General features
- Group 4 pulmonary hypertension
- Two subgroups
- Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH)
- Other pulmonary artery obstructions
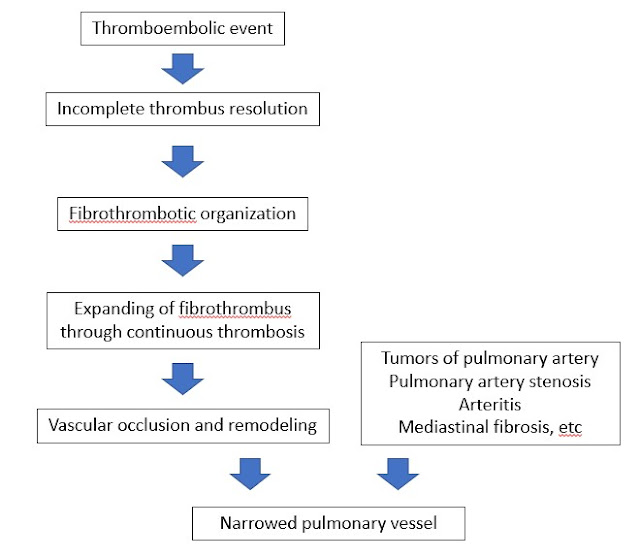
- Tumors of pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary artery stenosis
- Arteritis
- Mediastinal fibrosis, etc
Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension
- Definition
- Mean pulmonary arterial pressure > 20 mm Hg
- Presence of organized, nonacute, thromboembolic material and altered vascular remodeling in the pulmonary vasculature
- Rare but might be life threatening
- Likely due to underlying hypercoagulable state
- Commonly with history of pulmonary embolism
- Worse prognosis if > 70 years, residual PH, comorbidities, etc
Pathogenesis
- Incomplete thrombus resolution resulting organization and remodeling of pulmonary vessels
- Other causes resulting narrowing pulmonary vessels
Clinical presentations
- Features of pulmonary hypertension: progressive dyspnea, etc
- Features of thromboembolism
- History of acute pulmonary thromboembolic events
- History of acute deep veinous thromboembolic events
- Flow murmurs over the lung fields: due to partially obstructed vessels
Diagnosis
- Confirmation of pulmonary hypertension
- Chest radiography: Enlarged right ventricle
- Ventilation perfusion lung scan: Recommended initial study
- Pulmonary angiography: complete/partial vascular obstruction
- Laboratory tests: CBC, coagulation panels
Treatment
- Surgery: Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy
- Medical care
- If inoperable
- o Targeted therapy: Riociguat, macitentan, phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors, etc
- Improve right heart function: Diuretics
- Anticoagulation: Warfarin
- Long term monitoring: 6-minute walk distance testing, transthoracic echocardiography, right heart catheterization
Back to pulmonary hypertension
Back to contents
Comments
Post a Comment