Practice questions III Lung and pleural tumors
Practice questions III
Lung and pleural tumors
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
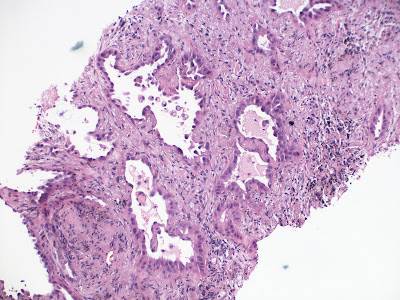
1. Use this case and this image for next three
questions. A 75-year-old woman presents with non-productive cough and a 15
lb weight loss in the past 6 months. She does not have fever or chest pain. She
has a history of clear cell type renal cell carcinoma at age 57 and was treated
with left nephrectomy. Her past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. She does
not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol. Radiologic examination reveals a 2.5 cm
lesion in the right middle lobe. An image of the biopsy is shown. There are
foci of necrosis with neutrophils. What is most likely the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Yale Rosen from USA, CC BY-SA 2.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
A. Abscess
B. Adenocarcinoma
C. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma
D. Small cell carcinoma
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
B. Adenocarcinoma
C. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma
D. Small cell carcinoma
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
2. A 75-year-old
woman presents with non-productive cough and a 15 lb weight loss in the past 6
months. She does not have fever or chest pain. She has a history of clear cell
type renal cell carcinoma at age 57 and was treated with left nephrectomy. Her
past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. She does not smoke cigarette
nor drink alcohol. Radiologic examination reveals a 2.5 cm lesion in the right
middle lobe. An image of the biopsy is shown. There are foci of necrosis with
neutrophils. What marker is most likely positive for this lesion?
(Image credit: Yale Rosen from USA, CC BY-SA 2.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
3. A 75-year-old
woman presents with non-productive cough and a 15 lb weight loss in the past 6
months. She does not have fever or chest pain. She has a history of clear cell
type renal cell carcinoma at age 57 and was treated with left nephrectomy. Her
past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. She does not smoke cigarette
nor drink alcohol. Radiologic examination reveals a 2.5 cm lesion in the right
middle lobe. An image of the biopsy is shown. There are foci of necrosis with
neutrophils. What molecular test should be performed next?
(Image credit: Yale Rosen from USA, CC BY-SA 2.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
A. ALK and EGFR
B. BHD and VHL
C. Mismatch repair (MMR) genes
D. NF1 and NF2
E. TSC1 and TSC2
B. BHD and VHL
C. Mismatch repair (MMR) genes
D. NF1 and NF2
E. TSC1 and TSC2
4. Use this case and this image for next three questions. A 65-year-old
man presents with anorexia and weakness for 2 weeks. He was diagnosed with
colon intramucosal adenocarcinoma at age 52 and was treated with endoscopic
mucosal resection. The resection margins were negative for malignancy per
pathology report. He has a history of hypertension and COPD. He smoked 1 and a
half pack cigarette per day for 30 years and quitted smoking 10 years ago,
after his COPD was diagnosed. He occasionally drinks wine. Physical examination
is unremarkable. Laboratory tests reveals a hemoglobin of 11.5 g/dl (14-18
g/dl), a serum calcium at 11.7 mg/dl (normal 8.6-11.2 mg/dl). Other lab results
are within normal range. Chest CT scan reveal a 3.5 cm mass at left lower lobe,
near hilum. Left hilar lymphadenopathy is noted as well. Image of his biopsy is
shown. What is most likely the diagnosis?
(Image source and license: https://www.flickr.com/photos/pulmonary_pathology/3923394574/in/photostream/)
E. Squamous cell
carcinoma
5. A 65-year-old man
presents with anorexia and weakness for 2 weeks. He was diagnosed with colon
intramucosal adenocarcinoma at age 52 and was treated with endoscopic mucosal
resection. The resection margins were negative for malignancy per pathology
report. He has a history of hypertension and COPD. He smoked 1 and a half pack
cigarette per day for 30 years and quitted smoking 10 years ago, after his COPD
was diagnosed. He occasionally drinks wine. Physical examination is
unremarkable. Laboratory tests reveals a hemoglobin of 11.5 g/dl (14-18 g/dl),
a serum calcium at 11.7 mg/dl (normal 8.6-11.2 mg/dl). Other lab results are
within normal range. Chest CT scan reveal a 3.5 cm mass at left lower lobe,
near hilum. Left hilar lymphadenopathy is noted as well. Image of his biopsy is
shown. What is marker is likely to be positive in this tumor?
(Image source and license: https://www.flickr.com/photos/pulmonary_pathology/3923394574/in/photostream/)
A. Chromogranin
B. CK20
C. p63
D. TTF-1
E. WT-1
B. CK20
C. p63
D. TTF-1
E. WT-1
6. A 65-year-old man
presents with anorexia and weakness for 2 weeks. He was diagnosed with colon
intramucosal adenocarcinoma at age 52 and was treated with endoscopic mucosal
resection. The resection margins were negative for malignancy per pathology
report. He has a history of hypertension and COPD. He smoked 1 and a half pack
cigarette per day for 30 years and quitted smoking 10 years ago, after his COPD
was diagnosed. He occasionally drinks wine. Physical examination is
unremarkable. Laboratory tests reveals a hemoglobin of 11.5 g/dl (14-18 g/dl),
a serum calcium at 11.7 mg/dl (normal 8.6-11.2 mg/dl). Other lab results are within
normal range. Chest CT scan reveal a 3.5 cm mass at left lower lobe, near
hilum. Left hilar lymphadenopathy is noted as well. Image of his biopsy is
shown. What is most likely the cause of his elevated serum calcium?
(Image source and license: https://www.flickr.com/photos/pulmonary_pathology/3923394574/in/photostream/)
A. Calcium-sensing receptor mutation
B. Ectopic production of parathyroid hormone related protein
C. Primary hyperparathyroidism
D. Secondary hyperparathyroidism
E. Vitamin D
toxicity
7. A 65-year-old man
presents with anorexia and weakness for 2 weeks. He was diagnosed with colon
intramucosal adenocarcinoma at age 52 and was treated with endoscopic mucosal
resection. The resection margins were negative for malignancy per pathology
report. He has a history of hypertension and COPD. He smoked 1 and a half pack
cigarette per day for 30 years and quitted smoking 10 years ago, after his COPD
was diagnosed. He occasionally drinks wine. Physical examination is
unremarkable. Laboratory tests reveals a hemoglobin of 11.5 g/dl (14-18 g/dl),
a serum calcium at 11.7 mg/dl (normal 8.6-11.2 mg/dl). Other lab results are
within normal range. Chest CT scan reveal a 3.5 cm mass at left lower lobe,
near hilum. Left hilar lymphadenopathy is noted as well. Image of his biopsy is
shown. What is most important risk factor for this lesion?
(Image source and license: https://www.flickr.com/photos/pulmonary_pathology/3923394574/in/photostream/)
8. Use this case and this image for next four
questions. A 61-year-old woman presents with double vision for 2 weeks. She
has had dry cough and a 15lb weight loss for the last three months. Her past
medical history is unremarkable. She does not smoke cigarette nor drink
alcohol. Upon physical examination, her right pupil is 4 mm in diameter, and
left pupil 6 mm in diameter. Her vision field and eye movement are normal.
Radiologic examination reveals a 2 cm solid mass at the apex of right upper
lobe. No other abnormalities are seen. Image of biopsy of the mass is shown.
Per immunohistochemistry studies, these cells are positive for CK7 and TTF-1,
but negative for CK5/6, vimentin and synaptophysin. What is the most likely
diagnosis?
(Image credit: Yale Rosen from USA, CC BY-SA 2.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>,
via Wikimedia Commons)
A. Adenocarcinoma
of lung
B. Large cell carcinoma
C. Mesothelioma, epithelioid type
D. Small cell carcinoma
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
B. Large cell carcinoma
C. Mesothelioma, epithelioid type
D. Small cell carcinoma
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
9. A 61-year-old
woman presents with double vision for 2 weeks. She has had dry cough and a 15lb
weight loss for the last three months. Her past medical history is
unremarkable. She does not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol. Upon physical
examination, her right pupil is 4 mm in diameter, and left pupil 6 mm in
diameter. Her vision field and eye movement are normal. Radiologic examination
reveals a 2 cm solid mass at the apex of right upper lobe. No other
abnormalities are seen. Image of biopsy of the mass is shown. Per
immunohistochemistry studies, these cells are positive for CK7 and TTF-1, but
negative for CK5/6, vimentin and synaptophysin. What additional test needs to
be performed?
(Image credit: Yale Rosen from USA, CC BY-SA 2.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>,
via Wikimedia Commons)
.jpg)
A. Chromogranin stain
B. EB virus studies
C. Molecular studies for EGFR mutation
D. Sputum Gram stain, culture and sensitivity
E. WT1 stain
10. A 61-year-old
woman presents with double vision for 2 weeks. She has had dry cough and a 15lb
weight loss for the last three months. Her past medical history is
unremarkable. She does not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol. Upon physical
examination, her right pupil is 4 mm in diameter, and left pupil 6 mm in
diameter. Her vision field and eye movement are normal. Radiologic examination
reveals a 2 cm solid mass at the apex of right upper lobe. No other
abnormalities are seen. Image of biopsy of the mass is shown. Per
immunohistochemistry studies, these cells are positive for CK7 and TTF-1, but
negative for CK5/6, vimentin and synaptophysin. What is most likely causing her
eye symptoms?(Image credit: Yale Rosen from USA, CC BY-SA 2.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
.jpg)
A. Autoantibody against postsynaptic acetylcholine receptor
B. Autoantibody against presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels
C. Local irritation of sympathetic nerve supply by the lung lesion
D. Metastatic tumor disrupt cranial nerve III
E. Metastatic tumor to right orbit
11. A 61-year-old
woman presents with double vision for 2 weeks. She has had dry cough and a 15lb
weight loss for the last three months. Her past medical history is
unremarkable. She does not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol. Upon physical
examination, her right pupil is 4 mm in diameter, and left pupil 6 mm in
diameter. Her vision field and eye movement are normal. Radiologic examination
reveals a 2 cm solid mass at the apex of right upper lobe. No other
abnormalities are seen. Image of biopsy of the mass is shown. Per
immunohistochemistry studies, these cells are positive for CK7 and TTF-1, but
negative for CK5/6, vimentin and synaptophysin. Abnormality of what gene is
likely seen?(Image credit: Yale Rosen from USA, CC BY-SA 2.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
12. Use this case and image for next two
questions. A 55-year-old man presents with worsening dry cough and intermittent
left chest pain for 3 months. He has lost 10 lb since then. He does not have
fever, chills and hemoptysis. His past medical history is unremarkable. He has
a 30-pack-year history of cigarette smoking and drinks 1-2 cups of liquor per
day. He works as a construction worker for 40 years. Physical examination
reveals no significant abnormalities except pallor skin. His CBC reveal a
hemoglobin of 9.5 g/dl (normal 14-18 g/dl) and a white count at 13.5 x 109/L
(normal 4.7 -10.5 x 109/L). Chest CT scan reveal a 3.1 cm mass of
left lower lobe, very close to the posterior edge. The mass is resected, and an
image of the microscopic examination is shown. Per immunohistochemistry
studies, these atypical cells are positive for pan-cytokeratin, but negative
for chromogranin, CD45, CD56, p63, TTF-1 and calretinin. What is the most
likely diagnosis?
(Image credit: The
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP), Public domain, via Wikimedia
Commons)

A. Large cell carcinoma
B. Hodgkin lymphoma
C. Mesothelioma
D. Small cell carcinoma
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
13. A 55-year-old
man presents with worsening dry cough and intermittent left chest pain for 3
months. He has lost 10 lb since then. He does not have fever, chills and
hemoptysis. His past medical history is unremarkable. He has a 30-pack-year
history of cigarette smoking and drinks 1-2 cups of liquor per day. He works as
a construction worker for 40 years. Physical examination reveals no significant
abnormalities except pallor skin. His CBC reveal a hemoglobin of 9.5 g/dl
(normal 14-18 g/dl) and a white count at 13.5 x 109/L (normal 4.7
-10.5 x 109/L). Chest CT scan reveal a 3.1 cm mass of left lower
lobe, very close to the posterior edge. The mass is resected, and an image of
the microscopic examination is shown. Per immunohistochemistry studies, these
atypical cells are positive for pan-cytokeratin, but negative for chromogranin,
CD45, CD56, p63, TTF-1 and calretinin. What risk factor is the most likely
associated with this lesion?
(Image credit: The
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons)
14. Use this case and image for next three
questions. A 59-year-man presents with fatigue, double vision and night
sweating for 1 month. He has lost 15 lb in the three months. His past medical
history is significant for chronic lymphocytic leukemia, hypertension and type
II diabetes. He has a 40 pack-year history of cigarette smoking. His vital
signs are within normal range except a blood pressure of 150/90 mm Hg. Physical
examination reveals mild bilateral eyelid ptosis and reduced muscle strength around
shoulder. His laboratory test results are within normal ranges except a hemoglobin
of 8.5 g/dl (14-18 g/dl). CT scan reveals a 3.5 cm mass in the hilar area of
right lung. Mediastinal lymphadenopathy is noted. Image of biopsy of this mass
is shown. Per immunohistochemistry studies, the cells are positive for
cytokeratin, but negative for CD45. What is the most likely diagnosis of this
mass?
(CC BY-SA 3.0
<http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/>, via Wikimedia Commons)
A. Diffuse large B
cell lymphoma
B. Hodgkin lymphoma
C. Small cell carcinoma
D. Small lymphocytic lymphoma
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
B. Hodgkin lymphoma
C. Small cell carcinoma
D. Small lymphocytic lymphoma
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
15. A 59-year-man
presents with fatigue, double vision and night sweating for 1 month. He has
lost 15 lb in the three months. His past medical history is significant for
chronic lymphocytic leukemia, hypertension and type II diabetes. He has a 40
pack-year history of cigarette smoking. His vital signs are within normal range
except a blood pressure of 150/90 mm Hg. Physical examination reveals mild bilateral
eyelid ptosis and reduced muscle strength around shoulder. His laboratory test
results are within normal ranges except a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (14-18 g/dl).
CT scan reveals a 3.5 cm mass in the hilar area of right lung. Mediastinal
lymphadenopathy is noted. Image of biopsy of this mass is shown. Per
immunohistochemistry studies, the cells are positive for cytokeratin, but
negative for CD45. What additional marker is likely to be positive for these
cells?
(CC BY-SA 3.0
<http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/>, via Wikimedia Commons)
16. A 59-year-man
presents with fatigue, double vision and night sweating for 1 month. He has
lost 15 lb in the three months. His past medical history is significant for
chronic lymphocytic leukemia, hypertension and type II diabetes. He has a 40
pack-year history of cigarette smoking. His vital signs are within normal range
except a blood pressure of 150/90 mm Hg. Physical examination reveals mild bilateral
eyelid ptosis and reduced muscle strength around shoulder. His laboratory test
results are within normal ranges except a hemoglobin of 8.5 g/dl (14-18 g/dl).
CT scan reveals a 3.5 cm mass in the hilar area of right lung. Mediastinal
lymphadenopathy is noted. Image of biopsy of this mass is shown. Per
immunohistochemistry studies, the cells are positive for cytokeratin, but
negative for CD45. What is the most likely cause of his reduced muscle strength?
(CC BY-SA 3.0
<http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/>, via Wikimedia Commons)
_by_core_needle_biopsy.jpg)
A. Autoantibody against acetylcholine receptor
B. Diabetic neuropathy
C. Irritation of sympathetic nerve supply
D. Muscular atrophy
E. Voltage-gated channel dysfunction
17. Use this case and this image for next two
questions. A 65-year-old man presents with slowing growing left anterior
neck mass for 3 month and progressive facial swelling, lightheadedness, blurred
vision and syncope for 2 weeks. He does not have history of heart disease or
seizures. He has had a 25 lb weight loss in one year. He does not smoke cigarette
nor drink alcohol. Physical examination reveals distended superficial jugular
veins and moderate edema of both arms, a 2.5 cm solid non mobile nodules at
right supraclavicular area. CT scan reveals a 3 cm mass at right upper lobe and
upper mediastinal lymphadenopathy. Image of the supraclavicular lesion is shown.
What is the diagnosis concerning the lymph node findings?
(Image credit: Nephron,
CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via
Wikimedia Commons)

A. Acute lymphadenitis
B. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
C. Hodgkin lymphoma
D. Metastatic lung adenocarcinoma
E. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
18. A 65-year-old man
presents with slowing growing left anterior neck mass for 3 month and progressive
facial swelling, lightheadedness, blurred vision and syncope for 2 weeks. He
does not have history of heart disease or seizures. He has had a 25 lb weight
loss in one year. He does not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol. Physical
examination reveals distended superficial jugular veins and moderate edema of
both arms, a 2.5 cm solid non mobile nodules at right supraclavicular area. CT
scan reveals a 3 cm mass at hilar area and upper mediastinal lymphadenopathy. Image
of the supraclavicular lesion biopsy is shown. What is causing the patient’s
presentation of facial swelling?
(Image credit: Nephron,
CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via
Wikimedia Commons)

A. Acute inflammation
B. Compression of superior vena cava
C. Congestive heart failure
D. Diffuse nonspecific chronic inflammation of subcutaneous tissue
E. Obstruction of lymph by metastatic tumor cells
19. Use this case and this image for next two
questions. A 71-year-old man presents with left chest pain, cough, weakness
and shortness of breath for 2 months. His past medical history is significant
for type 2 diabetes and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. He is a retired city
subway system maintenance worker after working for over 45 years. He has a 40
pack year history of cigarette smoking, but quitted after the diagnosis of COPD
at age 55. He drinks a glass of wine each day. Physical examination reveals
scattered crackles bilaterally. CT scan reveals a 2.5 cm left lower lobe mass at
the anterior edge. Image of the mass biopsy is shown. Per immunohistochemistry
studies, these cells are positive for CK5/6 and calretinin, but negative for
TTF-1. What is the diagnosis?
(Image Credit: Yale
Rosen from USA, CC BY-SA 2.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
.jpg)
A. Adenocarcinoma
B. Large cell carcinoma
C. Mesothelioma
D. Small cell carcinoma
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
20. A 71-year-old
man presents with left chest pain, cough, weakness and shortness of breath for
2 months. His past medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes and chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. He is a retired city subway system maintenance
worker after working for over 45 years. He has a 40 pack year history of
cigarette smoking, but quitted after the diagnosis of COPD at age 55. He drinks
a glass of wine each day. Physical examination reveals scattered crackles bilaterally.
CT scan reveals a 2.5 cm left lower lobe mass at the anterior edge. Image of the
mass biopsy is shown. Per immunohistochemistry studies, these cells are
positive for CK5/6 and calretinin, but negative for TTF-1. What is most likely
associated with this lesion?
(Image Credit: Yale
Rosen from USA, CC BY-SA 2.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)

Comments
Post a Comment