Practice question III Pathology of thyroid
Practice question III
Pathology of thyroid
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
1. Use this case and image for the next three questions. A 54-year-old woman presents with hoarseness for 3 months. She denies other symptoms. Her past medical history is unremarkable. She has a 30 pack-year history of cigarette smoking and is a social drinker. She denies usage of illicit drugs. Physical examination reveals left vocal cord paralysis. The mucosa of her vocal cords are unremarkable. No other abnormalities are seen. Laboratory tests are all within normal ranges. Sonographic examination reveals a 2.5 cm mass at the lower posterior portion of her left thyroid. Fine needle aspiration reveals small clusters of follicular cells without significant cytological atypia. Partial thyroidectomy was performed. An image of the microscopic findings is shown. No nuclear enlargement, nuclear inclusion or grooves are seen. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)])A. Follicular adenoma
B. Follicular carcinoma
C. Hashimoto thyroiditis
D. Multinodular goiter
E. Papillary carcinoma
2. A 54-year-old woman presents with hoarseness for 3 months. She denies other symptoms. Her past medical history is unremarkable. She has a 30 pack-year history of cigarette smoking and is a social drinker. She denies usage of illicit drugs. Physical examination reveals left vocal cord paralysis. The mucosa of her vocal cords are unremarkable. No other abnormalities are seen. Laboratory tests are all within normal ranges. Sonographic examination reveals a 2.5 cm mass at the lower posterior portion of her left thyroid. Fine needle aspiration reveals small clusters of follicular cells without significant cytological atypia. Partial thyroidectomy was performed. An image of the microscopic findings is shown. No nuclear enlargement, nuclear inclusion or grooves are seen. Abnormality of what gene is likely associated with these findings?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)])
A. BRAFB. PAX8
C. p53
D. RET-PTC
E. TSH receptor
3. A 54-year-old woman presents with hoarseness for 3 months. She denies other symptoms. Her past medical history is unremarkable. She has a 30 pack-year history of cigarette smoking and is a social drinker. She denies usage of illicit drugs. Physical examination reveals left vocal cord paralysis. The mucosa of her vocal cords are unremarkable. No other abnormalities are seen. Laboratory tests are all within normal ranges. Sonographic examination reveals a 2.5 cm mass at the lower posterior portion of her left thyroid. Fine needle aspiration reveals small clusters of follicular cells without significant cytological atypia. Partial thyroidectomy was performed. An image of the microscopic findings is shown. No nuclear enlargement, nuclear inclusion or grooves are seen. Damage of what structure is most likely associated with her hoarseness?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)])
B. Cricoid cartilage
C. Recurrent laryngeal nerve
D. Superior laryngeal nerve, internal branch
E. Vocal cord mucosa
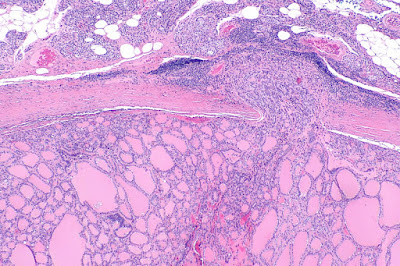
4. Use this case and image for the next four questions. A 23-year-old woman presents with anterior neck nodules for 2 years. She does not have other symptoms. Her past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals asymmetrically enlarged thyroid with nodular surface. Her laboratory tests, including TSH, T3 and T4 are within normal ranges. Sonographic examination reveals multiple nodular growth with various sizes, some with cystic changes. Biopsy of one of the nodules is shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: KGH assumed (based on copyright claims). [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)])
B. Graves disease
C. Hashimoto thyroiditis
D. Multinodular goiter
E. Papillary carcinoma
5. A 23-year-old woman presents with anterior neck nodules for 2 years. She does not have other symptoms. Her past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals asymmetrically enlarged thyroid with nodular surface. Her laboratory tests, including TSH, T3 and T4 are within normal ranges. Sonographic examination reveals multiple nodular growth with various sizes, some with cystic changes. Biopsy of one of the nodules is shown. What additional finding is likely seen?
(Image credit: KGH assumed (based on copyright claims). [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)])
B. Large follicle lined by flat cells
C. Marked lymphocytic infiltrate
D. Multifocal involvement
E. Pale colloid
6. A 23-year-old woman presents with anterior neck nodules for 2 years. She does not have other symptoms. Her past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals asymmetrically enlarged thyroid with nodular surface. Her laboratory tests, including TSH, T3 and T4 are within normal ranges. Sonographic examination reveals multiple nodular growth with various sizes, some with cystic changes. Biopsy of one of the nodules is shown. What molecular abnormality is likely seen in these cells?
(Image credit: KGH assumed (based on copyright claims). [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)])
B. Pax 8
C. PI3KCA
D. PTEN
7. A 23-year-old woman presents with anterior neck nodules for 2 years. She does not have other symptoms. Her past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals asymmetrically enlarged thyroid with nodular surface. Her laboratory tests, including TSH, T3 and T4 are within normal ranges. Sonographic examination reveals multiple nodular growth with various sizes, some with cystic changes. Biopsy of one of the nodules is shown. How this patient should be treated?
(Image credit: KGH assumed (based on copyright claims). [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)])
B. Inhibitors of thyroid hormone synthesis
C. Iodine supplementation
D. Thyroid hormone replacement
E. Total thyroidectomy
8. Use this case and image for the next question. A 71-year-old man presents with progressively enlarging anterior neck nodules for 2 months. He started having hoarseness for 1 week. He does not have other symptoms. His past history includes hypertension and coronary heart disease. He had a transurethral resection of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Pertinent physical examination findings include a 4.5 cm firm thyroid mass that is fixed to surrounding tissue. His laboratory test results are unremarkable. Image of biopsy of his neck mass is shown. No nuclear grooves or inclusions are noted. Per immunohistochemistry studies, these cells in solid nests are positive for cytokeratin, and p53, but negative for thyroglobulin, PSA and calcitonin. What is the most likely diagnosis?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)])A. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
B. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
C. Medullary carcinoma of thyroid
D. Metastatic prostatic adenocarcinoma
E. Papillary carcinoma
9. Use this case and image for the next four
questions. A 41-year-old man presents with anterior neck nodules for 5
months. He does not have other symptoms. His past medical history is
unremarkable. Physical examination reveals a 1.5 cm nodule in his left thyroid.
His CBC, TSH, T3, T4, liver and renal function tests are within normal ranges.
Sonographic exam reveals a well demarcated nodule in the lower portion of the
left lobe of thyroid. No other sonographic abnormalities are noted. Image of
biopsy of this nodule is shown. What additional stain should be performed?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
B. Congo red stain
C. Fungal stain
D. Serum test for anti-TSH receptor
E. Serum test for anti-peroxidase
10. A 41-year-old man presents with anterior neck nodules for 5 months. He does not have other symptoms. His past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals a 1.5 cm nodule in his left thyroid. His CBC, TSH, T3, T4, liver and renal function tests are within normal ranges. Sonographic exam reveals a well demarcated nodule in the lower portion of the left lobe of thyroid. No other sonographic abnormalities are noted. Image of biopsy of this nodule is shown.
Congo red stain reveal orange staining for the amorphous material, that has a green birefringence under polarized light. What additional marker is most likely expressed by these cells?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
B. CD3
C. Light chain
D. Parathyroid hormone
E. Thyroglobulin
11. A 41-year-old man presents with anterior neck nodules for 5 months. He does not have other symptoms. His past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals a 1.5 cm nodule in his left thyroid. His CBC, TSH, T3, T4, liver and renal function tests are within normal ranges. Sonographic exam reveals a well demarcated nodule in the lower portion of the left lobe of thyroid. No other sonographic abnormalities are noted. Image of biopsy of this nodule is shown.
Congo red stain reveal orange staining for the amorphous material, that has a green birefringence under polarized light. Per immunohistochemistry studies, these cells are positive for cytokeratin and calcitonin, and negative for thyroglobulin. Abnormality of what gene is likely found in this lesion?

(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
B. MEN1
C. PAX8
D. PTC
E. RET
12. A 41-year-old man presents with anterior neck nodules for 5 months. He does not have other symptoms. His past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals a 1.5 cm nodule in his left thyroid. His CBC, TSH, T3, T4, liver and renal function tests are within normal ranges. Sonographic exam reveals a well demarcated nodule in the lower portion of the left lobe of thyroid. No other sonographic abnormalities are noted. Image of biopsy of this nodule is shown.
Congo red stain reveal orange staining for the amorphous material, that has a green birefringence under polarized light. Per immunohistochemistry studies, these cells are positive for cytokeratin and calcitonin, and negative for thyroglobulin. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
B. Follicular carcinoma
C. Medullary carcinoma of thyroid
D. Papillary carcinoma of thyroid
E. Plasmacytoma
13. Use this case and image for the next question. A 47-year-old woman presents with anterior neck growth for 6 months. She does not have other symptoms. She was diagnosed with Hashimoto thyroiditis at age 31 and is currently taking levothyroxine. Physical examination reveals slight enlargement of her left thyroid. Her laboratory tests, including CBC, TSH, T3, T4, liver and renal function tests are within normal ranges. Sonographic exam reveals a 1 cm well demarcated nodule in the left lobe of her thyroid. Fine needle aspiration reveals small clusters of follicular cells with scant colloid. Partial thyroidectomy was performed and an image of the microscopic examination of this nodule is shown. No capsular or vascular invasion is noted. There is no evidence of nuclear abnormality. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Nephron [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)])
B. Follicular adenoma
C. Follicular carcinoma
D. Medullary carcinoma of thyroid
E. Papillary carcinoma of thyroid
14. Use this case and image for the next three questions. A 32-year-old woman presents with cold intolerance, and general weakness for 6 months. She has a 10 lb weight gain in the last 4 months. She was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes at age 19. Physical examination reveals slightly enlarged thyroid with smooth surface. No cervical lymphadenopathy is noted. She has mild bilateral ankle edema. Laboratory test reveals a TSH of 51 microIU/ml (normal 0.5-5 microIU/ml), free T3 at 1.1 pg/ml (normal 2.3-4.2 pg/ml). Her CBC is within normal ranges. An image of her thyroid biopsy is shown. What additional serum test is likely to be positive?
(Image credit: Librepath, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
B. Anti-thyroid peroxidase
C. Calcitonin
D. Chromogranin
E. Monoclonal immunoglobulin
15. A 32-year-old woman presents with cold intolerance, and general weakness for 6 months. She has a 10 lb weight gain in the last 4 months. She was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes at age 19. Physical examination reveals slightly enlarged thyroid with smooth surface. No cervical lymphadenopathy is noted. She has mild bilateral ankle edema. Laboratory test reveals a TSH of 51 microIU/ml (normal 0.5-5 microIU/ml), free T3 at 1.1 pg/ml (normal 2.3-4.2 pg/ml). Her CBC is within normal ranges. An image of her thyroid biopsy is shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Librepath, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
B. Graves disease
C. Hashimoto Thyroiditis
D. Multinodular goiter
E. Subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis
16. A 32-year-old woman presents with cold intolerance, and general weakness for 6 months. She has a 10 lb weight gain in the last 4 months. She was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes at age 19. Physical examination reveals slightly enlarged thyroid with smooth surface. No cervical lymphadenopathy is noted. She has mild bilateral ankle edema. Laboratory test reveals a TSH of 51 microIU/ml (normal 0.5-5 microIU/ml), free T3 at 1.1 pg/ml (normal 2.3-4.2 pg/ml). Her CBC is within normal ranges. An image of her thyroid biopsy is shown. What is the cause of her abnormal levels of TSH and free T3?
(Image credit: Librepath, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
B. Iodine deficiency
C. Systemic viral infection
D. TRH overproduction by hypothalamus
E. TSH secreting pituitary tumor
17. Use this case and image for the next three questions. A 21-year-old woman presents with a slowly enlarging painless lower anterior neck mass for 2 years. In the last 6 months, she gets tired easily, and has difficulty in concentration. She does not have fever, cough, change of voice or palpitation. Her past history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals bulging eyes and bilateral lid retraction. Her thyroid is soft and evenly enlarged with smooth surface. No cervical lymphadenopathy is noted. Laboratory test reveals a TSH of 0.01 microIU/ml (normal 0.5-5 microIU/ml), free T4 of 1.81 pg/ml (normal 0.79-1.34 pg/ml). Her CBC is within normal ranges. An image of her thyroid biopsy is shown. What additional serum test is likely to be positive?
(Image credit: Librepath, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
B. Anti-thyroid peroxidase
C. Calcitonin
D. Chromogranin
E. Inhibitory TSH receptor antibodies
18. A 21-year-old woman presents with a slowly enlarging painless lower anterior neck mass for 2 years. In the last 6 months, she gets tired easily, and has difficulty in concentration. She does not have fever, cough, change of voice or palpitation. Her past history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals bulging eyes and bilateral lid retraction. Her thyroid is soft and evenly enlarged with smooth surface. No cervical lymphadenopathy is noted. Laboratory test reveals a TSH of 0.01 microIU/ml (normal 0.5-5 microIU/ml), free T4 of 1.81 pg/ml (normal 0.79-1.34 pg/ml). Her CBC is within normal ranges. An image of her thyroid biopsy is shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Librepath, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
B. Graves disease
C. Hashimoto Thyroiditis
D. Multinodular goiter
E. Papillary carcinoma of thyroid
19. A 21-year-old woman presents with a slowly enlarging painless lower anterior neck mass for 2 years. In the last 6 months, she gets tired easily, and has difficulty in concentration. She does not have fever, cough, change of voice or palpitation. Her past history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals bulging eyes and bilateral lid retraction. Her thyroid is soft and evenly enlarged with smooth surface. No cervical lymphadenopathy is noted. Laboratory test reveals a TSH of 0.01 microIU/ml (normal 0.5-5 microIU/ml), free T4 of 1.81 pg/ml (normal 0.79-1.34 pg/ml). Her CBC is within normal ranges. An image of her thyroid biopsy is shown. What is the cause of her bulging eyes?
(Image credit: Librepath, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
B. Ectopic thyroid tissue in retro-orbital space
C. Retro-orbital connective tissues hypertrophy
D. Retro-orbital hemorrhage
E. Retro-orbital lymphocytic infiltration
20. Use this case and image for the next
question. A 51-year-old woman presents with gradual anterior neck swelling
for 3 years. She does not have other symptoms. Her past medical history is
unremarkable. Physical examination reveals an enlarged soft non-tender thyroid.
Her laboratory tests, including TSH, T3, T4 are within normal ranges.
Sonographic exam reveals multiple nodular growth in her thyroid, ranging from
0.5 to 3.7 cm. A biopsy of her thyroid is shown. No nuclear abnormality is
seen. What is the diagnosis?
B. Follicular adenoma
C. Follicular carcinoma
D. Medullary carcinoma of thyroid
E. Multinodular goiter
F. Papillary carcinoma of thyroid
Back to pathology of thyroid
Back to contents
.jpg)





Comments
Post a Comment