Practice questions Oral cavity pathology
Practice questions
Oral cavity pathology
Updated: 02/28/2019
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
1. A 35-year-old man
presents with a firm left gum nodule for 3 months. His past medical history is
unremarkable. He has a 15 pack-year history of cigarette smoking. He does not
drink alcohol. Physical examination reveals a 0.7 cm firm polypoid mass with
focal erosion and exudates. The mass is removed. Microscopically it has a
fibrous core with slightly hyperplastic smooth squamous lining. The squamous
epithelium has parakeratosis and mild cytological atypia. What is the
diagnosis?
A. Erythroplakia
B. Irritation fibroma
C. Pyogenic granuloma
D. Squamous cell carcinoma
E. Squamous papilloma
2. A 15-year-old boy
presents with painful lesion of his left lateral tongue. He has a history of
infectious mononucleosis a year ago. Physical examination reveals an isolated
0.2 cm shallow ulcer at the left anterolateral tongue. The ulcer has
well-defined erythematous edge. No other abnormalities are noted. What is
likely the diagnosis?
A. Aphthous ulcer
B. Erythroplakia
C. Hairy leukoplakia
D. Herpes
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
3. A 32-year-old man
presents with palate pain for 2 days. He had a cold 1 week ago and recovered
spontaneously. His past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination
reveals clusters of small ulcers covered by purulent exudates at the right hard
and soft palate. Tzanck smears reveals multinucleated cells with ground glass
appearing nuclear matrix and dark stain along nuclear membrane. What is the
diagnosis?
A. Aphthous ulcer
B. Erythroplakia
C. Hairy leukoplakia
D. Herpes
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
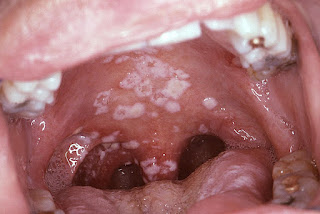
4. Use the image for this
question. A 48-year-old man presents with white painful growth on his palate.
He has type 2 diabetes but not compliant with his diet recommendations. He has
a 30 pack-year history of cigarette smoking and has been drinking 2 glasses
wine per day for 10 years. An image of his oral cavity is shown. After these
patches are scraped, there is erythematous base. No ulcer is noted. What is the
diagnosis?
A. Candidiasis
B. Erythroplakia
C. Hairy leukoplakia
D. Herpes
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
5. A 21-year-old woman
presents with a rapidly growing left gingiva mass for a month. Her past medical
history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals a 0.5 cm fragile purple
polypoid growth for focal ulceration. The growth is removed. Microscopically,
it has a lobular pattern of capillary growth separated by fibrous septa. No
endothelial atypia is noted. What is the diagnosis?
A. Angiosarcoma
B. Irritation fibroma
C. Pyogenic granuloma
D. Squamous cell carcinoma
E. Squamous papilloma
6. Use this
case for the next two questions. A 34-year-old homosexual man presents of
painful white growth at his left lateral tongue. He is HIV positive and is
currently being treated with antiretroviral agents. He has a 10 pack-year
history of cigarette smoking, but does not drink alcohol. Physical examination
reveals diffuse thick which patch along the left border of his tongue. No
ulceration is noted. The patch is non-movable and non-scrapable. No other
abnormalities are noted. Biopsy of the lesion reveals hyperkeratotic squamous
mucosa containing large squamous cells with abundant pale cytoplasm. No
cytoplasmic halo nor nuclear pleomorphism is seen. What is the diagnosis?
A. Candidiasis
B. Erythroplakia
C. Hairy leukoplakia
D. Squamous cell carcinoma
E. Squamous papilloma
7. A 34-year-old homosexual man presents of painful
white growth at his left lateral tongue. He is HIV positive and is currently
being treated with antiretroviral agents. He has a 10 pack-year history of
cigarette smoking, but does not drink alcohol. Physical examination reveals
diffuse thick which patch along the left border of his tongue. No ulceration is
noted. The patch is non-movable and non-scrapable. No other abnormalities are
noted. Biopsy of the lesion reveals hyperkeratotic squamous mucosa containing
large squamous cells with abundant pale cytoplasm. No cytoplasmic halo nor
nuclear pleomorphism is seen. What is most likely associated with these
findings?
A. Cigarette smoking
B. EB virus
C. Human herpes virus
D. Human immunodeficiency virus
E. Human papillomavirus
8. Use this
case for the next two questions. A 44-year-old woman presents with painless
white growth at her floor of mouth for 2 months. She has type 2 diabetes and
hypertension. She has been smoking cigarette 1 pack a day for 20 years. She is
a social drinker. Physical examination reveals a thick white patch at the right
side of her floor of mouth. This patch is non-movable and non-scrapable, and
has a warty appearance. No other abnormalities are noted. What is most likely
the diagnosis?
A. Candidiasis
B. Erythroplakia
C. Hairy leukoplakia
D. Leukoplakia
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
9. A 44-year-old woman presents with painless white
growth at her floor of mouth for 2 months. She has type 2 diabetes and
hypertension. She has been smoking cigarette 1 pack a day for 20 years. She is
a social drinker. Physical examination reveals a thick white patch at the right
side of her floor of mouth. This patch is non-movable and non-scrapable, and
has a warty appearance. No other abnormalities are noted. What is the next step
of management?
A. Anti-fungal therapy
B. Anti-viral therapy
C. Biopsy
D. Surgery
E. Topical steroid
10. Use this
case for the next two questions. A 51-year-old woman was referred from a
local dental office for evaluation of redness at her left buccal mucosa. Her
past medical history is unremarkable. She does not smoke cigarette nor drink
alcohol, but has been chewing tobacco for 30 years. Physical examination
reveals an irregular 2.2 cm reddish patch at her left buccal mucosa. The patch
is non-movable and non-scrapable, and has a velvety appearance. The surrounding
mucosa appears to be normal. No firm mass is noted. What is most likely the
diagnosis?
A. Candidiasis
B. Erythroplakia
C. Hairy leukoplakia
D. Lichen planus
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
11. A 51-year-old woman was referred from a local
dental office for evaluation of redness at her left buccal mucosa. Her past
medical history is unremarkable. She does not smoke cigarette nor drink
alcohol, but has been chewing tobacco for 30 years. Physical examination
reveals an irregular 2.2 cm reddish patch at her left buccal mucosa. The patch
is non-movable and non-scrapable, and has a velvety appearance. The surrounding
mucosa appears to be normal. No firm mass is noted. What is the next step of
management?
A. Anti-fungal therapy
B. Anti-viral therapy
C. Biopsy
D. Surgery
E. Topical steroid
12. A 55-year-old man presents with painful ulcer at
the left tongue for 6 months. He has a history of type 2 diabetes. He has been
chewing betel nuts since age of 18, but does not smoke cigarette nor drink
alcohol. Physical examination reveals a 1.3 cm ulceration at the left edge of
his tongue. This ulcer has an irregular indurated edge and is covered by white
greyish debris. Biopsy of the ulcer reveals irregular nests of markedly
atypical cells with recognizable intercellular bridge and irregular concentric
layers of atypical cells. What is the diagnosis?
A. Candidiasis
B. Erythroplakia
C. Herpes
D. Lichen planus
E. Squamous cell carcinoma
Back to oral
cavity pathology
Back to contents
Comments
Post a Comment