Practice questions B Stomach pathology
Practice questions B
Stomach pathology
Updated: 03/01/2019
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
1. Use this
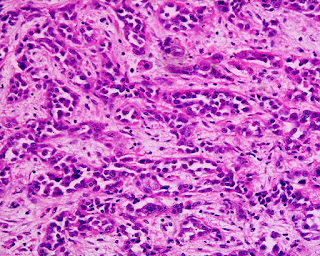
case and this image for the next 4 questions. A 69-year-old man presents
with intermittent epigastric discomfort for 4 weeks. He has a history of coronary
heart disease and received bypass grafting 5 years ago. His past medical
history also include diabetes, hypertension, and helicobacter gastritis.
Physical examination, laboratory tests and complete cardiac tests are
unremarkable. Gastroscopy examination reveals a 1.5 cm ulcer at the antrum. The
ulcer has a raised irregular edge. Image of the ulcer biopsy is shown. What is
the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Kwz~commonswiki)
A. Curling ulcer
B. Cushing ulcer
C. Diffuse type adenocarcinoma
D. Intestinal type adenocarcinoma
E. Peptic ulcer
2. A 69-year-old man presents with intermittent
epigastric discomfort for 4 weeks. He has a history of coronary heart disease and
received bypass grafting 5 years ago. His past medical history also include
diabetes, hypertension, and helicobacter gastritis. Physical examination, laboratory
tests and complete cardiac tests are unremarkable. Gastroscopy examination
reveals a 1.5 cm ulcer at the antrum. The ulcer has a raised irregular edge.
Image of the ulcer biopsy is shown. What in his history is most likely associated
with his antral lesion?
(Image credit: Kwz~commonswiki)
A. Coronary bypass grafting
B. Diabetes
C. Helicobacter gastritis
D. Hypertension
3. A 69-year-old man presents with intermittent
epigastric discomfort for 4 weeks. He has a history of coronary heart disease and
received bypass grafting 5 years ago. His past medical history also include
diabetes, hypertension, and helicobacter gastritis. Physical examination, laboratory
tests and complete cardiac tests are unremarkable. Gastroscopy examination
reveals a 1.5 cm ulcer at the antrum. The ulcer has a raised irregular edge.
Image of the ulcer biopsy is shown. Abnormality of what intracellular component
is most likely associated with this antral lesion?
(Image credit: Kwz~commonswiki)
A. Beta-catenin
B. CDH1
C. C-kit
D. Gastrin
E. MEN1
4. A 69-year-old man presents with intermittent
epigastric discomfort for 4 weeks. He has a history of coronary heart disease and
received bypass grafting 5 years ago. His past medical history also include
diabetes, hypertension, and helicobacter gastritis. Physical examination, laboratory
tests and complete cardiac tests are unremarkable. Gastroscopy examination
reveals a 1.5 cm ulcer at the antrum. The ulcer has a raised irregular edge.
Image of the ulcer biopsy is shown. Additional immunohistochemistry studies
reveal nuclear located beta-catenin in these glandular cells in this image, but
not those on the surface. What causes this finding?
(Image credit: Kwz~commonswiki)
A. Adhesins
B. CagA
C. Urease
D. VacA
5. Use this
case and this image for the next 2 questions. A 39-year-old man presents
with indigestion and left upper abdomen discomfort for 3 months. His past
medical history is unremarkable. He has a family history of stomach cancer and helicobacter
gastritis. Physical examination reveal vague tenderness at left upper abdomen. Gastroscopy
exam reveals slightly thickened rugae. No erythema, ulcer nor tumor is noted. An
image of the biopsy is shown. What is the diagnosis?
(Image credit: Nephron/wiki
commons)
A. Acute gastritis
B. Chronic gastritis
C. Diffuse type adenocarcinoma
D. Intestinal type adenocarcinoma
E. Menetrier’s disease
6. A 39-year-old man presents with indigestion and
left upper abdomen discomfort for 3 months. His past medical history is
unremarkable. He has a family history of stomach cancer and helicobacter
gastritis. Physical examination reveal vague tenderness at left upper abdomen. Gastroscopy
exam reveals slightly thickened rugae. No erythema, ulcer nor tumor is noted. An
image of the biopsy is shown. Mutation of what gene is likely identified?
(Image credit: Nephron/wiki
commons)
A. APC
B. Beta-catenin
C. CDH-1
D. EGFR
E. Her2
7. A 45-year-old woman presents with vague epigastric
discomfort for 3 months. She has a history helicobacter gastritis. Physical
examination and laboratory tests are unremarkable. Gastroscopy examination
reveals a 0.7 cm nodule at her fundus. The nodule has smooth unremarkable surface.
No other abnormalities are noted. Biopsy of the nodule reveals fundic type
gastric mucosa with irregular trabeculae of cells with small to intermediate
sized round nuclei and stippled chromatin and moderate amount of cytoplasm. No
significant pleomorphism is seen. Per immunohistochemistry studies, these cells
are positive for chromogranin. What is the diagnosis?
A. Carcinoid
B. Diffuse type adenocarcinoma
C. Helicobacter gastritis
D. Intestinal type adenocarcinoma
E. Small cell carcinoma
8. Use this
case and this image for the next 2 questions. A 44-year-old woman presents
with vague epigastric pain for 6 months. She has a history of Hashimoto
thyroiditis and autoimmune gastritis. She does not smoke cigarette nor drink
alcohol. Physical examination and laboratory test results are unremarkable. Gastroscopy
examination reveals a bulging mass at the gastric body. The mass has a normal appearing
mucosal surface. No ulcer nor erythematous changes are noted. Biopsy of the
mass reveals a spindle cell proliferation with unremarkable mucosal epithelium
and glands. These spindle cells are positive for CD34. No significant
cytological atypia is noted. What is the diagnosis?
A. Chronic gastritis with smooth muscle proliferation
B. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor
C. Intestinal type adenocarcinoma
D. Leiomyoma
E. Leiomyosarcoma
9. A 44-year-old woman presents with vague epigastric
pain for 6 months. She has a history of Hashimoto thyroiditis and autoimmune
gastritis. She does not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol. Physical examination
and laboratory test results are unremarkable. Gastroscopy examination reveals a
bulging mass at the gastric body. The mass has a normal appearing mucosal
surface. No ulcer nor erythematous changes are noted. Biopsy of the mass
reveals a spindle cell proliferation with unremarkable mucosal epithelium and
glands. These spindle cells are positive for CD34. No significant cytological
atypia is noted. Mutation of what gene is likely associated with these
findings?
A. APC
B. Beta-catenin
C. CDH-1
D. C-kit
E. Her2
10. Use this
case and this image for the next 2 questions. A 58-year-old man presents
with fatigue, nausea and vague epigastric pain for 2 months. He has a history of
peptic ulcer and prostate adenocarcinoma. He does not smoke cigarette nor drink
alcohol. Physical examination and laboratory tests are unremarkable.
Gastroscopy exam reveals a 2.3 cm ulcer at the greater curvature and thickened surrounding
mucosa. Biopsy of the ulcer reveals dense small to intermediate sized lymphocytic
infiltrate. No cytological atypia is seen in the epithelial cells. Silver stain
is negative for microorganism. His carbon 13/14 urea breath test is positive.
Per immunohistochemistry studies, these lymphocytes are positive for CD20,
CD45, negative for CD3, CD5 and CD10, and have predominant kappa light chain
expression. What is the diagnosis?
A. Autoimmune gastritis
B. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
C. Marginal zone lymphoma
D. Peptic ulcer
E. Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma
11. A 58-year-old man presents with fatigue, nausea
and vague epigastric pain for 2 months. He has a history of peptic ulcer and prostate
adenocarcinoma. He does not smoke cigarette nor drink alcohol. Physical
examination and laboratory tests are unremarkable. Gastroscopy exam reveals a
2.3 cm ulcer at the greater curvature and thickened surrounding mucosa. Biopsy
of the ulcer reveals dense small to intermediate sized lymphocytic infiltrate. No
cytological atypia is seen in the epithelial cells. Silver stain is negative
for microorganism. His carbon 13/14 urea breath test is positive. Per
immunohistochemistry studies, these lymphocytes are positive for CD20, CD45, negative
for CD3, CD5 and CD10, and have predominant kappa light chain expression. What
is most likely causing his gastric changes?
A. Androgen
B. Autoantibody against parietal cells
C. Helicobacter pylori
D. Hypergastrinemia
E. NSAID
E. NSAID
12. Use this
case and this image for the next 2 questions. A 76-year-old man presents
with progressive weakness, night sweating, a 15 pound weight loss and vague
epigastric discomfort for 4 months. He has a history of COPD, diabetes,
hypertension and helicobacter gastritis. Physical examination reveals no
significant abnormalities, except for pale skin. Laboratory tests reveal a
hemoglobin of 7.5 g/dl (normal 13.5-18 g/dl). Other tests, including liver and
renal function tests, are within normal range. Peripheral blood smear reveals
no morphological abnormalities. Gastroscopy examination reveal 3 ulcers at the
fundus and antrum. Biopsy of the ulcers reveal acute and chronic inflammation.
Sheets of markedly atypical cells are seen. These cells are positive for CD20
and negative for cytokeratin. What is the diagnosis?
A. Autoimmune gastritis
B. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
C. Marginal zone lymphoma
D. Peptic ulcer
E. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
13. A 76-year-old man presents with progressive
weakness, night sweating, a 15 pound weight loss and vague epigastric
discomfort for 4 months. He has a history of COPD, diabetes, hypertension and helicobacter
gastritis. Physical examination reveals no significant abnormalities, except
for pale skin. Laboratory tests reveal a hemoglobin of 7.5 g/dl (normal 13.5-18
g/dl). Other tests, including liver and renal function tests, are within normal
range. Peripheral blood smear reveals no morphological abnormalities.
Gastroscopy examination reveal 3 ulcers at the fundus and antrum. Biopsy of the
ulcers reveal acute and chronic inflammation. Sheets of markedly atypical cells
are seen. These cells are positive for CD20 and negative for cytokeratin. What is
most likely associated with these changes?
A. COPD
B. Diabetes
C. Helicobacter pylori
D. Hypergastrinemia
E. Hypertension
Back to stomach
pathology
Back to contents

Comments
Post a Comment