Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba histolytica
Updated: 01/26/2024
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
General features
- A protozoan transmitted by ingestion of amebic cysts
- Fecal-oral transmission usually through food or water
- Most cases asymptomatic, while up to 100k death annually
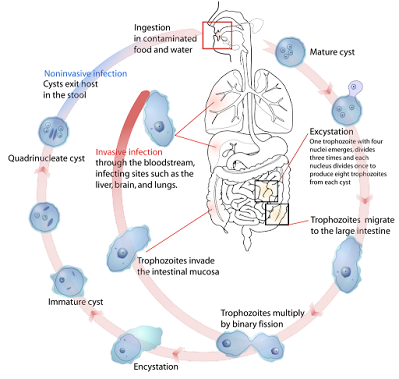
Life cycle
Key clinical features
- Intestinal amebiasis and extraintestinal manifestations
- Bloody diarrhea due to colonic tissue damage
- Presentation depends on locations of infection
-
Gastrointestinal: Gradual onset,
fever, abdominal pain, tenesmus, diarrhea (with or without blood), dysentery
- Liver: Abscess, most common extraintestinal complication; fever, right upper quadrant pain, hepatomegaly with hepatic tenderness; may rupture and involve surrounding structures
- Respiratory tract: Rare, atelectasis and pleural effusions
- Brain: Abscesses, very rare, sudden onset symptoms such as headache, vomiting, and mental status changes with rapid progression to death
Colonoscopic findings
Pathologic findings
Diagnosis
- Stool microscopy: poor sensitivity, cyst or trophozoites
- Stool antigen detection
- Serology: high sensitivity and specificity, not helpful in distinguishing between an acute or previous infection
- Stool molecular studies: high sensitivity and specificity, more expensive
Treatment
- First-line treatment: Metronidazole
Back to Infectious gastroenteritis
Back to Contents
Comments
Post a Comment