Practice question answers, skin tumors 2
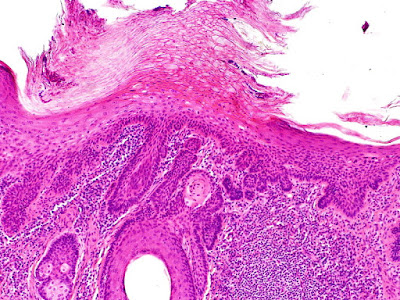
Practice question answers, skin tumors 2 © Jun Wang, MD, PhD 1. A. Dysplasia limited to basal layer is most consistent with actinic keratosis . Basal cell carcinoma has irregular budding, nest, cords of basaloid cells with scant cytoplasm with peripheral palisading. Bowen disease has full thickness dysplasia. Dermatophytosis is fungal infection and has intraepidermal neutrophilic infiltration but not keratinocytic atypia. Melanoma in situ has Pagetoid spread of atypical melanocytes. 2. E. Actinic keratosis is a squamous precancerous lesion and may develop into squamous cell carcinoma or basal cell carcinoma . 3. E. This lesion has irregular nest, cords of basaloid cells with scant cytoplasm with peripheral palisading, characteristic for basal cell carcinoma . The most important carcinogenic factor for melanoma , squamous cell carcinoma or basal cell carcinoma is UV light from sun exposure. Abnormal keratinocytic turnover is seen various lesions, including psoria