Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease
Autosomal Recessive (Childhood) Polycystic Kidney Disease
Updated: 10/01/2021
© Jun Wang,
MD, PhD
General features
- Many patients die shortly after birth
- Cause of death: Secondary respiratory insufficiency due to pulmonary hypoplasia
- Prognosis depends on kidney and liver involvements
Key pathogenesis
- Probably abnormal centromere duplication and mitotic spindle assembly during cell division
- Developmental defects of collecting ducts
- Developmental defects of hepatobiliary ductal plate remodeling
key clinical features
- Presentations associated with kidney and liver dysfunction
- Oligohydramnios
- Pulmonary hypoplasia: Respiratory distress
- Portal hypertension
- Potter syndrome
Results of severe
oligohydramnios
Limb deformities:
club feet, hip dislocation, etc
Facial
appearances: pseudoepicanthus, recessed chin, posteriorly rotated, flattened
ears, and flattened nose
Pulmonary hypoplasia
Laboratory findings:
- High BUN/Creatinin
- Hyponatremia: Renal dysfunction
Key pathological findings
- Kidney
Enlarged kidneys
with smooth surface
Cystic dilatation
of renal collecting ducts
Dilatation in both
cortex and medulla
Cysts lined by
flat or cuboidal cells
- Liver
Congenital hepatic
fibrosis in portal area
Increased bile ducts around portal perimeter
- Pulmonary hypoplasia
Genetic abnormalities
- PKHD1 mutation: encode polyductin, AKA fibrocystin
Diagnosis
- Radiologic studies: Markedly enlarged kidneys with poor corticomedullary differentiation
- Genetic testing: PKHD1 mutation
Differential diagnosis
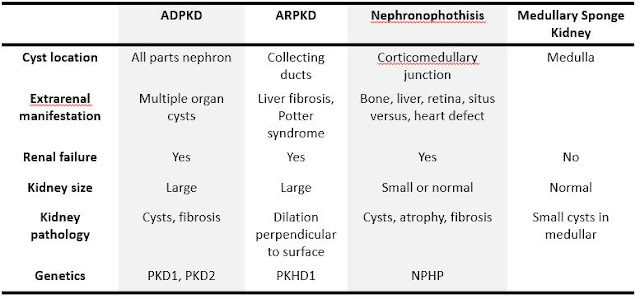
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: Cystic changes involving other organs, but NO congenital liver fibrosis
- Glomerulocystic cortical cysts: Associated with tuberous sclerosis, trisomy 13 etc
- Nephronophthisis: Normal or small sized kidney, NPHP gene mutation, cysts at corticomedullary junction, etc
Treatment
- Perinatal: Prenatal consultation, delivery at places with neonatal intensive care
- Neonatal: Respiratory stabilization, renal function monitoring, managements for hypertension and hyponatremia, etc
- Infancy and childhood: Care of renal and hepatic complications
Back to kidney
masses
Back to contents
Comments
Post a Comment