Breast carcinoma
Breast carcinoma
Updated: 02/14/2020
© Jun Wang,
MD, PhD
General feature
- Most common cancer in women, regardless of race or ethnicity
- Second most common cause of death from cancer in women
- Mortality reducing due to early detection by mammogram
Etiology
- Genetic
- Hormonal: most commonly associated risk factor
Higher risk group
- Age: risk increases with age until age 80
- Personal history of breast cancer
- Inherited genetic mutations for breast cancer
- History of atypical hyperplasia
- Mammographically dense breasts
Intermediate risk group
- High endogenous estrogen or testosterone levels, etc
Carcinogenesis
- Estrogen dependent: most common, ER+
- Her2 associated: most common in Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- ER, Her2 independent
Molecular abnormalities
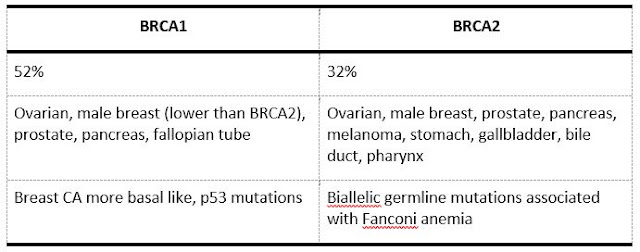
- Hereditary Breast and Ovary Cancer syndrome: BRCA1 and BRCA2
- Her2
- p53
- CHEK2
- PTEN: Cowden syndrome
- STK11, as seen in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
- ATM
- CDH1 in lobular carcinoma
- DNA mismatch repair genes (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2): Lynch syndrome
Molecular subtypes
- Luminal A: ER+, PR+, her2-
- Luminal B: ER+, PR+, her2+
- Her2+: ER-, PR-, her2+
- Basal like: ER-, PR-, her2-, CK5/6+
- Unclassified
Most common clinical features
- Mass
- Abnormal mammogram findings
Categories per morphology
- Paget disease
- Carcinoma in situ
- Invasive carcinoma
- Others, including sarcoma, lymphoma
Ancillary test
- Estrogen receptor
- Progesterone receptor
- Her2
- Proliferative index by ki67
Categories per ancillary test results
- ER positive Her2 negative, low proliferation
Older woman, men, mammogram detected
Well to moderately differentiated
Good prognosis
- ER positive Her2 negative, high proliferation
BRCA
mutation carriers
Poorly differentiated
Intermediate prognosis
- Her2 positive
ER may be positive or negative
Young women, non white
p53
mutation
Early relapse
Rare survival with metastasis
- ER negative Her2 negative
Not the same as basal like, even similar
Medullary, adenoid cystic, secretory,
metaplastic
Young women, non white
BRCA1
mutation carriers
Rare survival with metastasis
Management
- Ductal carcinoma in situ, pleomorphic lobular carcinoma in situ: Surgery, hormonal, radiation
- Classic lobular carcinoma in situ: Watchful waiting, probably hormonal therapy
- Invasive carcinoma: surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy
Back to breast pathology
Back to contents
Comments
Post a Comment