Sjögren syndrome
Sjögren syndrome
Updated: 02/13/2021
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
General features
- Third most common rheumatic disorder, after rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus
- Typically presents with xerostomia, keratoconjunctivitis sicca (dry eye), rheumatoid arthritis, and hepergammaglobulinemia
- More common in women, average onset between 40-60
- May involve lymph nodes, lung, kidney, etc
- Associated with Graves disease, Hashimoto thyroiditis, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, especially MALT lymphoma
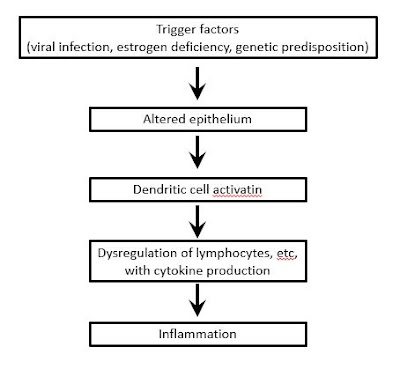
Pathogenesis
Clinical features
- Xerostomia (dry mouth)
- Keratoconjunctivitis sicca (dry eyes)
- Enlarged parotid glands
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Hypergammaglobulinemia
Diagnostic criteria
- Inclusion criteria: At least one symptom of ocular or oral dryness
- Exclusion criteria
- History of head and neck radiation treatment
- Active hepatitis C infection
- Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
- Sarcoidosis
- Amyloidosis
- Graft-verses-host disease
- IgG4-related disease
Pathological features
- Lymphoid infiltrate, often interstitial fibrosis and acinar atrophy
- Probably epimyoepithelial islands (proliferation of salivary gland ductal epithelium and myoepithelium) in major salivary glands
Management
- Relieving symptoms
·
Back to contents

Comments
Post a Comment