Melanoma
Melanoma
Updated: 03/10/2023
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
General
features
- Malignancy of melanocytes, predominantly in skin
- May involve eyes, ears, GI tract, leptomeninges, mucous membranes
- Majority of skin cancer deaths
- More common in older population
- Strong association with UV light (sun or artificial) exposure
- Melanoma in situ: Atypical melanocytes limited in epidermis
- Invasive melanoma: Atypical melanocytes invade into dermis and beyond
- Prognostic factors: depth of invasion (Clark’s levels or Breslow thickness), nodal status, etc
- Thin: < 1 mm
- Moderate: 1-4 mm
- Thick: > 4 mm
Risk factors
- Excessive UV light exposure, including indoor tanning
- Living closer to the equator or at a higher elevation
- History of sunburn
- Fair skin
- Multiple nevi or dysplastic nevi
- Family history of melanoma
- Weakened immune system
Pathogenesis
- Complex
Pro-growth
signaling pathway: RAS/BRAF, PI3K-ATK/PTEN, Gain of function
Cell cycle
control: CDKN2A (p14, p16) Loss of function, cKIT (over-expression)
Telomerase activity: TERT promoters, Gain of function
Clinical
features
- Change in color, size, symptoms of pigmented lesion
- Development of new pigmented lesion in adult life
- Irregular borders, variegation of color in pigmented lesion
- May be amelanotic: subtle pigmentation
- Hutchinson's sign:
Periungual
extension of brown-black pigmentation
onto the proximal and lateral nail folds
May be seen
associated with benign melanocytic nevi, subungual hematomas, Bowen’s disease
Pathological
features
- Asymmetrical and poorly demarcated
- Melanocytes beyond basal layer, single or in nests
- Atypical melanocytes in dermis
Epithelioid: polygonal cells
Spindled: elongated
nuclei
- Two phases of growth
Radial phase:
horizontal spread of tumor cells
Vertical phase:
downward invasion
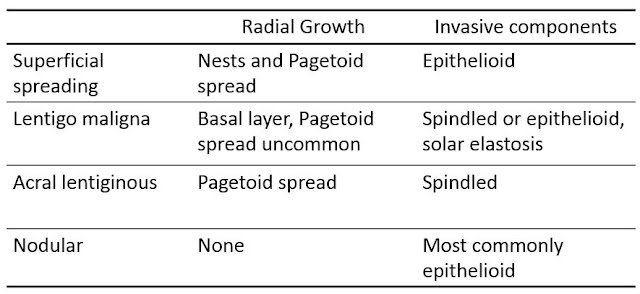
- Four major subtypes of melanoma
Superficial
spread: Slight elevated, or flat growth
Lentigo maligna: Usually flat growth
Acral
lentiginous: Acral skin, more common in people with darker skin
Nodular: Rapid growth, aggressive clinical course, smooth nodules covered by normal epidermis, well demarcated nodules of malignant melanocytes,
Marker
- Positive: S100, HMB45, melan A, tyrosinase
- Negative: cytokeratin
Differential
diagnosis
- Non melanocytic: Morphology and negative reactivity to HMB45, MelanA and S100
- Granular cell tumor: Negative for HMB45 and MelanA
- Amelanotic melanoma: resemble pyogenic granuloma, positive for S100, HMB45
- Nevi: normal maturation, symmetry, no atypia, no Pagetoid spread, no necrosis
- Paget’s disease: Positive for CK7 and CAM5.2, Negative for HMB45, MelanA and S100
Management
- Surgery
- Immune therapy: Antibodies against CTLA4 and PD1
- Targeted therapy: BRAF w/ or w/o MEK inhibitor; KIT inhibitor
- Chemotherapy
- Interferon alpha
Back to skin
tumors
Back to skin
pathology
Back to contents
Comments
Post a Comment