Malignant neoplasms of lungs
Malignant neoplasms of lung
Updated: 07/11/2022
© Jun Wang, MD, PhD
General features
- Leading cause of cancer death in the United States
- Cessation of smoking improves prognosis
- Metastasis commonly to adrenal glands, brain, contralateral lung, bone, liver, etc
Risk factors
- Cigarette smoking: Most common risk factor; quantity of cigarette smoking summarized by the number of packs of cigarettes smoked per day multiplied by the number of years smoked
- Secondhand smoke
- Radiation at home: Radon
- Occupational and environmental factors: wood/coal fuels, asbestos, arsenic, radiation, dusts and fumes from nickel, chromium, etc
- Family and genetic factors
Clinical presentations
- Coughing
- Hemoptysis
- Chest pain
- Others: Pneumonia, pleural effusion, etc
- Superior vena cava syndrome
Medical
emergency and most often manifests in patients with a malignant disease
process within the thorax
Due to obstruction of blood flow through the
superior vena cava
May cause obstructive shock
Requires immediate diagnostic evaluation and
therapy
Presentations: Dyspnea (most common), facial
swelling, head fullness, arm swelling,
etc
Management: Relieve symptoms and to attempt cure of the primary malignant process, corticosteroids, diuretics,
radiation therapy, surgical bypass, etc
- Horner syndrome
Caused by interruption of the sympathetic nerve supply to the eye
Classic triad of miosis (ie, constricted pupil), partial ptosis, and loss of
hemifacial sweating (ie, anhidrosis)
Causes: Neuronal defects, trauma, tumors or
infection of the lung apex,
dissecting aneurysm, etc
Treatment: Treat underlying diseases
Diagnostic approach
- Clinical assessment: history, PE, any signs of metastasis
- Laboratory: CBC, electrolytes, calcium, alkaline phosphatase, etc
- Image studies
- Pathological studies: Biopsy, sputum cytology, etc
Current classification
- Epithelial tumors
Adenocarcinoma, including large cell carcinoma
Adenosquamous cell carcinoma, sarcomatoid
carcinoma, salivary gland type tumor, etc
- Mesenchymal tumors
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor
Synovial sarcoma
Myoepithelial tumor, etc
- Lymphohistiocytic tumors: Lymphomas, etc
- Tumors of ectopic origin: Teratoma, etc
- Metastatic tumors: Most common malignant tumor of lungs, usually multiple, express markers of original tumor
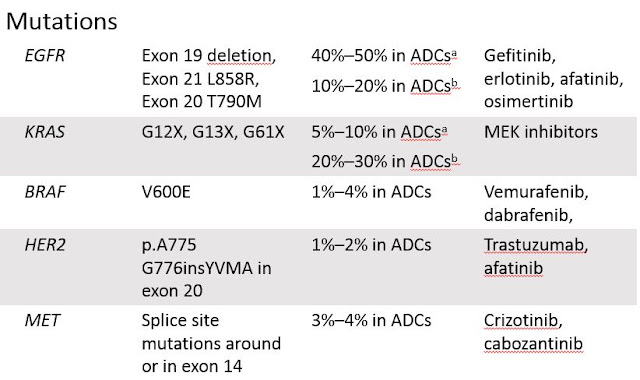
Molecular abnormalities
- KRAS: GTPase, RAS/MAPK pathway
- EGFR: Protein tyrosine kinase
- EML4-ALK fusion: Consistent activation of ALK tyrosine kinase domain
- Others: Including BRAF, Her2, PIK3CA, etc
Current molecular tests and targeted therapies
aAsian populations; bWestern populations
Treatment
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
Indicators for poor prognosis
- High stage at presentation
- Poor performance scores
- Weight loss
Back to contents

Comments
Post a Comment