Practice questions Oral cavity pathology
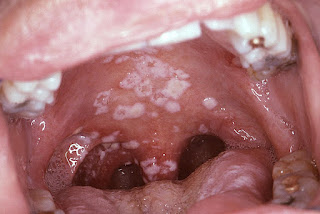
Practice questions Oral cavity pathology Updated: 02/28/2019 © Jun Wang, MD, PhD 1. A 35-year-old man presents with a firm left gum nodule for 3 months. His past medical history is unremarkable. He has a 15 pack-year history of cigarette smoking. He does not drink alcohol. Physical examination reveals a 0.7 cm firm polypoid mass with focal erosion and exudates. The mass is removed. Microscopically it has a fibrous core with slightly hyperplastic smooth squamous lining. The squamous epithelium has parakeratosis and mild cytological atypia. What is the diagnosis? A. Erythroplakia B. Irritation fibroma C. Pyogenic granuloma D. Squamous cell carcinoma E. Squamous papilloma 2. A 15-year-old boy presents with painful lesion of his left lateral tongue. He has a history of infectious mononucleosis a year ago. Physical examination reveals an isolated 0.2 cm shallow ulcer at the left anterolateral tongue. The ulcer has well-defined erythematous edge. No other abnormalities