Pulmonary hypertension with unclear and/or multifactorial mechanisms
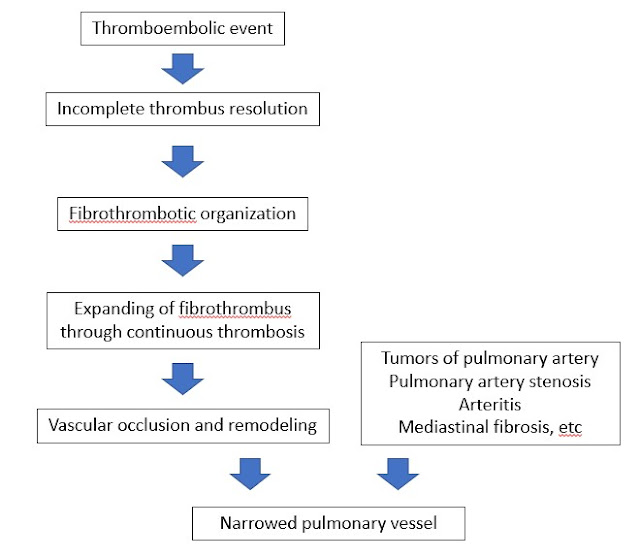
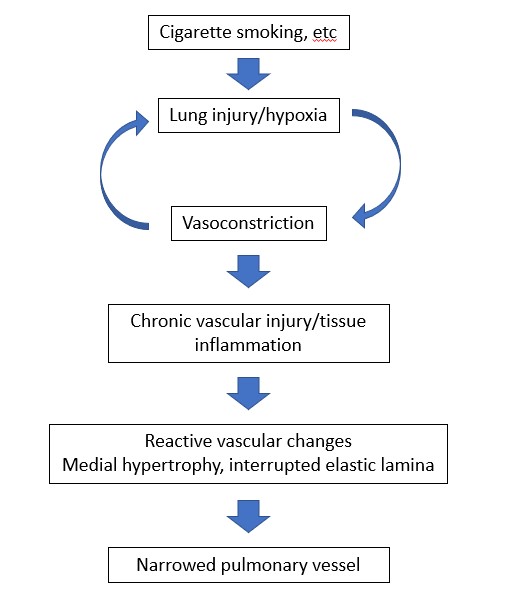
Pulmonary hypertension with unclear and/or multifactorial mechanisms Updated: 08/31/2022 © Jun Wang, MD, PhD General features Group 5 pulmonary hypertension Associated with various disorders Hematologic disorders: MPNs, postsplenectomy, sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, etc Systemic disorders: Sarcoidosis, pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis Metabolic disorders: Autoimmune thyroid disease, glycogen storage disease, Gaucher disease Other disorders: End-stage renal disease Complex congenital heart disease Pathogenesis Pathogenesis not well understood Clinical presentations Presentations of pulmonary hypertension Presentations of underlying lung diseases Treatment Management of underlying etiology Back to pulmonary hypertension Back to contents