Practice questions 2 Infectious gastroenteritis
Practice questions 2
Infectious gastroenteritis
©Jun Wang, MD, PhD
1.
Use this case and image for next 2
questions. A 41-year-old man presents to the emergency department with vomiting,
diarrhea, and leg cramps for a day. He recently returned from a trip to a developing
area and consumed seafood from street vendors. He appears critically ill and sluggish
in communicating. His blood pressure is 85/55 mmHg, heart rate is 140 beats per
minute. His eyes are sunken, and his skin and oral mucosa are dry. Laboratory
tests reveal a hematocrit of 60% (normal 40-54%) and a serum bicarbonate level
of 18 mmol/L (normal range: 22-28 mmol/L). An image of his stool is shown. What
is the most likely pathogen?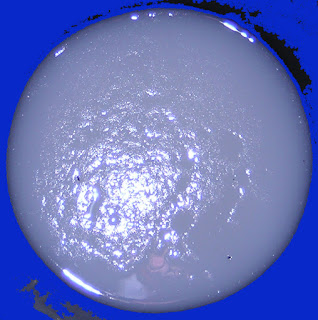
(Image credit: F1jmm, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
A.
Campylobacter jejuni
B.
Entamoeba histolytica
C.
Enterotoxigenic E. coli
D.
Giardia intestinalis
E.
Shigella
F.
Vibrio Cholerae
2.
A 41-year-old man presents to the emergency department with vomiting, diarrhea,
and leg cramps for a day. He recently returned from a trip to a developing area
and consumed seafood from street vendors. He appears critically ill and sluggish
in communicating. His blood pressure is 85/55 mmHg, heart rate is 140 beats per
minute. His eyes are sunken, and his skin and oral mucosa are dry. Laboratory
tests reveal a hematocrit of 60% (normal 40-54%) and a serum bicarbonate level
of 18 mmol/L (normal range: 22-28 mmol/L). An image of his stool is shown. What
is the cause of his low blood pressure?

(Image
credit: F1jmm, CC BY-SA 3.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
A.
Abnormal dilatation of vessels
B.
Diffuse microthrombi formation
C.
Impaired right heart diastolic filling
D.
Left ventricular dysfunction
E.
Reduced circulating volume
3.
Use this case for the next 4 questions. A 28-year-old female presents to
the clinic with abdominal cramps and frequent, small-volume bloody stools for
two days. She recently traveled to a developing country and consumed street
food. Her past medical history is unremarkable. On examination, she appears acutely
ill, with a temperature of 101.8°F (38.8°C). Abdominal examination reveals
tenderness on palpation in the left lower quadrant. Initial stool microscopy
shows abundant polymorphonuclear leukocytes and red blood cells. No cysts or
trophozoites are seen. What test can be done for a fast diagnosis?
A. Clostridium difficile test
B. Colonoscopic examination and biopsy
C. Darkfield microscopic examination of stool
D. Molecular tests for enterotoxin LT
E. Multiplex molecular panels
F. Shiga toxin test
4.
A 28-year-old female presents to the clinic with abdominal cramps and frequent,
small-volume bloody stools for two days. She recently traveled to a developing
country and consumed street food. Her past medical history is unremarkable. On
examination, she appears acutely ill, with a temperature of 101.8°F (38.8°C).
Abdominal examination reveals tenderness on palpation in the left lower
quadrant. Initial stool microscopy shows abundant polymorphonuclear leukocytes
and red blood cells. No cysts or trophozoites are seen.
Multiplex
molecular tests reveal pathogen suspicious for Shigella or salmonella. What additional test should be done to confirm the
diagnosis?
A.
Clostridium difficile test
B.
Colonoscopic examination and biopsy
C.
Darkfield microscopic examination of stool
D.
Shiga toxin test
E.
Stool culture
5.
A 28-year-old female presents to the clinic with abdominal cramps and frequent,
small-volume bloody stools for two days. She recently traveled to a developing
country and consumed street food. Her past medical history is unremarkable. On
examination, she appears acutely ill, with a temperature of 101.8°F (38.8°C).
Abdominal examination reveals tenderness on palpation in the left lower
quadrant. Initial stool microscopy shows abundant polymorphonuclear leukocytes
and red blood cells. No cysts or trophozoites are seen.
Stool
culture at 37°C reveals
Gram-negative, non lactose-fermenting bacilli that do not produce H2S.
How would this pathogen spread between colonic epithelium?
A.
Cause host cell apoptosis and membrane damage
B.
Direct invasion from apical surface
C.
Form fibrin-rich deposits on the surface of epithelial cells
D.
Promote formation of intracellular actin jet trail
E.
Utilize flagellar motility
6.
A 28-year-old female presents to the clinic with abdominal cramps and frequent,
small-volume bloody stools for two days. She recently traveled to a developing
country and consumed street food. Her past medical history is unremarkable. On
examination, she appears acutely ill, with a temperature of 101.8°F (38.8°C).
Abdominal examination reveals tenderness on palpation in the left lower
quadrant. Initial stool microscopy shows abundant polymorphonuclear leukocytes
and red blood cells.
Stool
culture at 37°C
reveals Gram-negative, non lactose-fermenting bacilli that do not
produce H2S. What is the pathogen?
A.
Campylobacter jejuni
B.
Entamoeba histolytica
C.
Enterotoxigenic E. coli
D.
Salmonella enterica
E.
Shigella
F.
Vibrio Cholerae
7.
Use this case for the next 4 questions. A 35-year-old man presents to
the clinic with abdominal cramps and non-bloody diarrhea for three days. He started
having fever in the past 24 hours. Prior to these presentations, he ate a
reheated chicken dish a few days ago. On examination, the patient is alert with
mild stress. He has a temperature of 101.5°F. His other vital signs are within
normal ranges. Physical examinations reveals mild abdominal tenderness. What test
should be done to confirm the diagnosis?
A.
Clostridium difficile test
B.
Colonoscopic examination and biopsy
C.
Darkfield microscopic examination of stool
D.
Shiga toxin test
E.
Stool culture
8.
A 35-year-old man presents to the clinic with abdominal cramps and non-bloody
diarrhea for three days. He started having fever in the past 24 hours. Prior to
these presentations, he ate a reheated chicken dish a few days ago. On
examination, the patient is alert with mild stress. He has a temperature of 101.5°F.
His other vital signs are within normal ranges. Physical examinations reveals
mild abdominal tenderness. What test should be done to confirm the diagnosis?
Stool
culture at 37°C
reveals Gram-negative, catalase-positive, oxidase-negative, bacilli
that produce H2S. What is most likely the pathogen?
A.
Campylobacter jejuni
B.
Entamoeba histolytica
C.
Enterotoxigenic E. coli
D.
Salmonella enterica
E.
Shigella
F.
Vibrio Cholerae
9.
A 35-year-old man presents to the clinic with abdominal cramps and non-bloody
diarrhea for three days. He started having fever in the past 24 hours. Prior to
these presentations, he ate a reheated chicken dish a few days ago. On
examination, the patient is alert with mild stress. He has a temperature of 101.5°F.
His other vital signs are within normal ranges. Physical examinations reveals
mild abdominal tenderness. What test should be done to confirm the diagnosis?
Stool
culture at 37°C
reveals Gram-negative, catalase-positive, oxidase-negative, bacilli
that produce H2S. Which part of the GI tract does this pathogen
start invasion?
A.
Cecum
B.
Duodenum
C.
Jejunum
D.
Ileum
E.
Colon
10.
A 35-year-old man presents to the clinic with abdominal cramps and non-bloody
diarrhea for three days. He started having fever in the past 24 hours. Prior to
these presentations, he ate a reheated chicken dish a few days ago. On
examination, the patient is alert with mild stress. He has a temperature of 101.5°F.
His other vital signs are within normal ranges. Physical examinations reveals
mild abdominal tenderness. What test should be done to confirm the diagnosis?
Stool
culture at 37°C
reveals Gram-negative, catalase-positive, oxidase-negative, bacilli
that produce H2S. What is the direct cause of his diarrhea?
A.
Colonic vascular endothelial damage
B.
Increased cAMP
C.
Invasion of jejunal mucosa
D.
Malabsorption
E.
Suppression of normal colonic flora
11.
Use this case for the next 4 questions. A 31-year-old woman presents to the
emergency department with complaints of watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and
low-grade fever for one days. Her stool is watery with a distinct foul odor. She
was diagnosed with urinary tract infection a week ago and is taking oral antibiotics.
Her significant past history include type 1 diabetes, Hashimoto thyroiditis, obesity
and irregular uterine bleeding. She has a temperature of 100.5°F. Her other
vital signs are within normal ranges. Abdominal examination reveals mild
tenderness, but there is no rebound or guarding. What test should be done to
confirm the diagnosis?
A.
Clostridium difficile exotoxin tests
B.
Colonoscopic examination and biopsy
C.
Darkfield microscopic examination of stool
D.
Shiga toxin test
E.
Stool culture
12.
A 31-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with complaints of
watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and low-grade fever for one days. Her stool
is watery with a distinct foul odor. She was diagnosed with urinary tract
infection a week ago and is taking oral antibiotics. Her significant past
history include type 1 diabetes, Hashimoto thyroiditis, obesity and irregular
uterine bleeding. She has a temperature of 100.5°F. Her other vital signs are within
normal ranges. Abdominal examination reveals mild tenderness, but there is no
rebound or guarding.
Her
clostridium difficile exotoxin test is positive for toxin B, but negative for
toxin A. What is the most likely pathogen?
A.
Campylobacter jejuni
B.
Clostridium difficile
C.
Enterotoxigenic E. coli
D.
Salmonella enterica
E.
Shigella
F.
Vibrio Cholerae
13.
A 31-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with complaints of
watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and low-grade fever for one days. Her stool
is watery with a distinct foul odor. She was diagnosed with urinary tract
infection a week ago and is taking oral antibiotics. Her significant past
history include type 1 diabetes, Hashimoto thyroiditis, obesity and irregular
uterine bleeding. She has a temperature of 100.5°F. Her other vital signs are within
normal ranges. Abdominal examination reveals mild tenderness, but there is no
rebound or guarding.
Her
clostridium difficile exotoxin test is positive for toxin B, but negative for
toxin A. What is the most likely cause of her diarrhea?
A.
Activation of guanylate cyclase
B.
Colonic mucosal injury
C.
Increased cAMP
D.
Invasion of jejunal mucosa
E.
Malabsorption
14.
A 31-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with complaints of
watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and low-grade fever for one days. Her stool
is watery with a distinct foul odor. She was diagnosed with urinary tract
infection a week ago and is taking oral antibiotics. Her significant past
history include type 1 diabetes, Hashimoto thyroiditis, obesity and irregular
uterine bleeding. She has a temperature of 100.5°F. Her other vital signs are within
normal ranges. Abdominal examination reveals mild tenderness, but there is no
rebound or guarding.
Her
clostridium difficile exotoxin tests is positive for toxin B, but negative for
toxin A. What is the most significant risk factor for her diarrhea?
A.
Antibiotics usage
B.
Estrogen effects
C.
Hypothyroidism
D.
Overweight
E.
Type 1 diabetes
15.
Use this case and image for next 4
questions. A 25-year-old man presents to the clinic with progressively
worsening abdominal pain and diarrhea for the past two weeks. He has loose stools
containing visible blood. He returned from a trip to a tropical region before
these symptoms. His past medical history is unremarkable. He appears fatigued and
his vital signs are within normal ranges, except for a temperature of 100.5°F.
There is tenderness over the lower abdomen without rebound or guarding. What
laboratory tests should be performed to confirm the diagnosis?
A.
Clostridium difficile exotoxin tests
B.
Darkfield microscopic examination of stool
C.
Regular light microscopic examination of stool
D.
Shiga toxin test
E.
Stool culture
16.
A 25-year-old man presents to the clinic with progressively worsening abdominal
pain and diarrhea for the past two weeks. He has loose stools containing
visible blood. He returned from a trip to a tropical region before these
symptoms. His past medical history is unremarkable. He appears fatigued and his
vital signs are within normal ranges, except for a temperature of 100.5°F. There
is tenderness over the lower abdomen without rebound or guarding.
An
image of his stool microscopic exam is shown. What is the cause of his diarrhea?

(Image
credit: The Other 95%, CC BY-SA 4.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
A.
Activation of guanylate cyclase
B.
Colonic mucosal injury
C.
Increased cAMP
D.
Invasion of jejunal mucosa
E.
Malabsorption
17.
A 25-year-old man presents to the clinic with progressively worsening abdominal
pain and diarrhea for the past two weeks. He has loose stools containing
visible blood. He returned from a trip to a tropical region before these
symptoms. His past medical history is unremarkable. He appears fatigued and his
vital signs are within normal ranges, except for a temperature of 100.5°F. There
is tenderness over the lower abdomen without rebound or guarding.
An
image of his stool microscopic exam is shown. What is most likely the source of
his infection?

(Image
credit: The Other 95%, CC BY-SA 4.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
A.
Beef
B.
Chicken
C.
Rice
D.
Seafood
E.
Water
18.
A 25-year-old man presents to the clinic with progressively worsening abdominal
pain and diarrhea for the past two weeks. He has loose stools containing
visible blood. He returned from a trip to a tropical region before these
symptoms. His past medical history is unremarkable. He appears fatigued and his
vital signs are within normal ranges, except for a temperature of 100.5°F. There
is tenderness over the lower abdomen without rebound or guarding.
An
image of his stool microscopic exam is shown. What is the pathogen?

(Image
credit: The Other 95%, CC BY-SA 4.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
A.
Entamoeba histolytica
B.
Enterotoxigenic E. coli
C.
Giardia intestinalis
D.
Salmonella enterica
E.
Shigella
F.
Vibrio Cholerae
19.
Use this case and image for next 4
questions. A 25-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with diarrhea
and abdominal discomfort for the past two weeks. She describes the diarrhea as
foul-smelling, greasy, and accompanied by excessive gas. She went hiking and
drank stream water in a remote area a month ago. Her vital signs are within normal
ranges. On examination, she is well-nourished and alert. There is no evidence of
dehydration. Abdominal examination reveals mild tenderness in the right upper
quadrant. What test can be done for a quick diagnosis?
A.
Clostridium difficile exotoxin tests
B.
Darkfield microscopic examination of stool
C.
Regular light microscopic examination of stool
D.
Shiga toxin test
E.
Stool culture
20.
A 25-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with diarrhea and
abdominal discomfort for the past two weeks. She describes the diarrhea as
foul-smelling, greasy, and accompanied by excessive gas. She went hiking and
drank stream water in a remote area a month ago. Her vital signs are within normal
ranges. On examination, she is well-nourished and alert. There is no evidence of
dehydration. Abdominal examination reveals mild tenderness in the right upper
quadrant.
Microscopic
exam of her stool reveals finding similar to the image shown. What is the direct
cause of her diarrhea?
(Image
credit: Kalumet, CC BY-SA 4.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
A.
Activation of guanylate cyclase
B.
Colonic mucosal injury
C.
Increased cAMP
D.
Invasion of jejunal mucosa
E.
Malabsorption
21.
A 25-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with diarrhea and
abdominal discomfort for the past two weeks. She describes the diarrhea as
foul-smelling, greasy, and accompanied by excessive gas. She went hiking and
drank stream water in a remote area a month ago. Her vital signs are within normal
ranges. On examination, she is well-nourished and alert. There is no evidence of
dehydration. Abdominal examination reveals mild tenderness in the right upper
quadrant.
Microscopic
exam of her stool reveals finding similar to the image shown. What is the pathogen
of her diarrhea?

(Image
credit: Kalumet, CC BY-SA 4.0
<https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons)
A.
Entamoeba histolytica
B.
Enterotoxigenic E. coli
C.
Giardia intestinalis
D.
Salmonella enterica
E.
Shigella
F.
Vibrio Cholerae
Answers
Back to Infectious
gastroenteritis
Back to contents
Comments
Post a Comment