Cor pulmonale

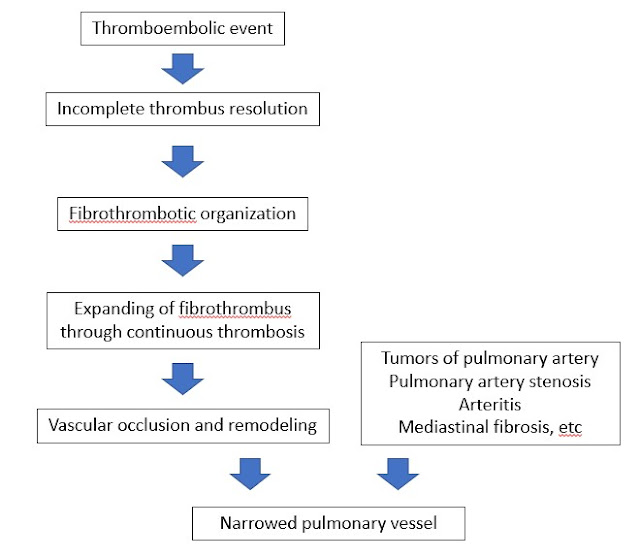
Cor pulmonale Updated:09/06/2022 © Jun Wang, MD, PhD General features Latin word: Pulmonary heart Alteration in the structure and function of the right ventricle of the heart Caused by a primary disorder of the respiratory system Commonly associated with pulmonary hypertension Commonly chronic and progressive clinical course Acute cor pulmonale may be life threatening Etiology Acute: Pulmonary embolism (most common), acute respiratory distress syndrome Chronic: Pulmonary hypertension Risks Any conditions that may increase pulmonary artery pressure Diseases of the pulmonary parenchyma Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Disorders of the pulmonary vessels Pulmonary hypertension Disorders affecting chest movement Kyphoscoliosis Marked obesity Neuromuscular diseases Disorders inducing pulmonary arterial constriction Metabolic acidosis Hypoxemia Pathogenesis Clinical presentations Associated with right heart failure Dyspnea on exertion: Most common Fatigue, let